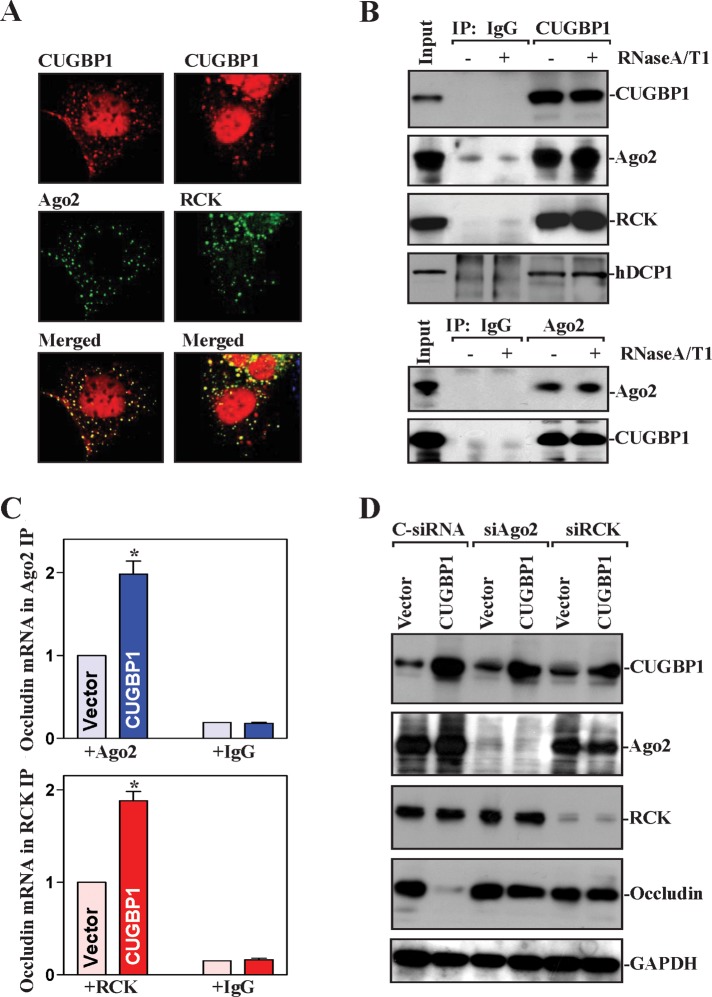
FIGURE 6:
CUGBP1 promotes interaction of the occludin mRNA with components of P-bodies. (A) Fluorescence analysis of CUGBP1 colocalization with PB-resident proteins Ago2 and RCK. Red (top), antibody detecting CUGBP1; green (middle), antibodies detecting Ago2 and RCK; yellow (bottom), merging of the two signals. (B) Physical interaction of CUGBP1 with PB component proteins. IP of protein complexes were performed on intact lysates (–) or lysates that had been incubated with both RNase A and RNase T1 (+), using IgG or antibody against CUGBP1 (top) or Ago2 (bottom). The levels of CUGBP1, Ago2, RCK, and hDCP1 were examined by Western blot analysis. (C) Effect of CUGBP1 on occludin mRNA interaction with components of PBs. After cells were transfected with the CUGBP1 expression vector or control vector for 48 h, the association of occludin mRNA with Ago2 or RCK was measured by RNP IP using anti-Ago2 (top) or RCK (bottom) antibodies, which was followed by Q-PCR analysis. Values are means ± SEM of data from three separate experiments. * p < 0.05 compared with cells transfected with control vector. (D) Effect of silencing Ago2 and RCK on occludin expression in cells overexpressing CUGBP1. Cells were transfected with CUGBP1 expression vector or cotransfected with the CUGBP1 and specific siRNA targeting Ago2 (siAgo2) or RCK (siRCK); 48 h later, the levels of CUGBP1, Ago2, RCK, and occludin proteins were assessed by Western blot analysis. Equal loading was monitored by blotting GAPDH.