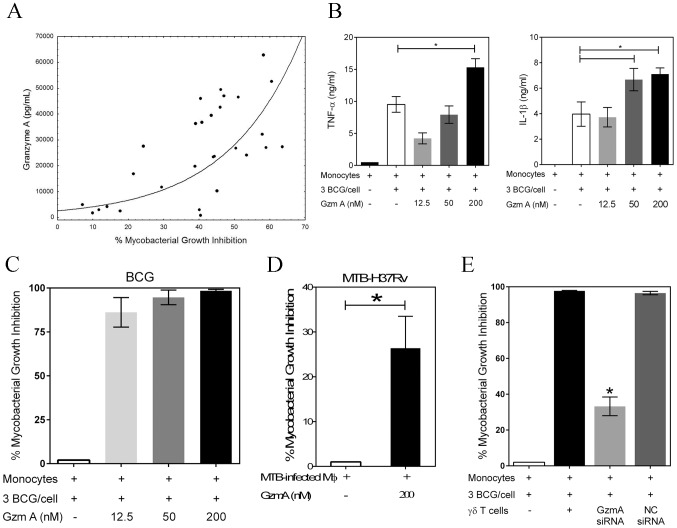
Figure 3. Granzyme A secretion by γ9δ2 T cells mediates inhibition of intracellular mycobacteria by induction of inflammatory responses in mycobacteria-infected macrophages.
A, The levels of granzyme A produced by γ9δ2 T cells are directly and highly correlated with inhibition of intracellular mycobacterial growth (r = 0.7564; p<0.0001). Supernatant levels of granzyme A, measured by CBA, were correlated with the level of mycobacterial growth inhibition observed in γ9δ2 T cell co-cultures with BCG-infected macrophages. B, Purified granzyme A induces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β by BCG-infected macrophages (*p<0.05, n = 4; statistical comparisons performed using Friedman's test). The indicated concentrations of purified granzyme A were added to BCG-infected monocytes for 3 days and the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in the culture supernatants determined by CBA. C-D, Purified granzyme A alone can induce inhibition of intracellular mycobacterial growth in the absence of perforin. The indicated concentrations of granzyme A were added to BCG-infected (C) or M. tuberculosis H37Rv-infected (D) co-cultures for 3 days and the surviving bacteria quantified by H3-uridine incorporation and CFU counting. (*p<0.03; n = 6–12 by Wilcoxon matched pairs test comparing levels of mycobacterial intracellular growth in cultures with and without added purified granzyme A). Purified granzyme A had no direct effects on extracellular mycobacterial growth (data not shown). E, siRNA knockdown of granzyme A in γ9δ2 T cells reduces the inhibitory activity of γ9δ2 T cells for mycobacterial growth (*p<0.05; n = 3 by one-way ANOVA comparing levels of intracellular mycobacterial growth inhibition in cultures with or without γ9δ2 T cells producing granzyme A). γ9δ2 T cells transduced with the indicated siRNA-lentivirus targeting GzmA or a negative control (NC) were co-cultured with BCG-infected macrophages for 3 days and surviving bacteria quantified by H3-uridine incorporation.