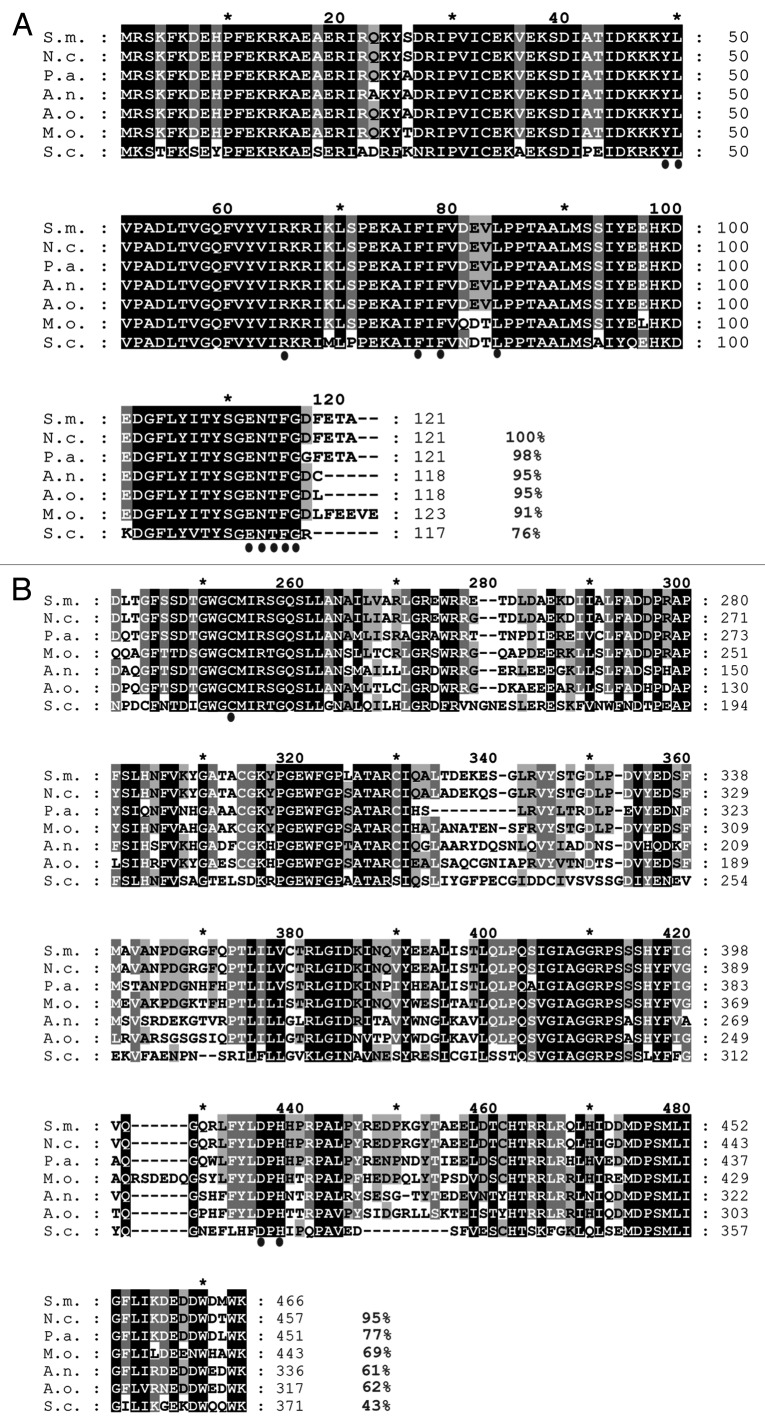
Figure 1. Multiple sequence alignment of the Atg8 and Atg4 proteins from members of the Ascomycota. (A) Amino acid alignment of Atg8 proteins. The ClustalX alignment was created using the following sequences: S.m., Sordaria macrospora, F7VP68; N.c., Neurospora crassa, Q8WZY7; P.a., Podospora anserina, Q8J282; A.n., Aspergillus nidulans, Q5B2U9; A.o., Aspergillus oryzeae, Q2UBH5; M.o., Magnaporthe oryzae, Q51MW4; S.c. Saccharomyces cerevisiae, P38182. Conserved residues important for the interaction with Atg4 and Atg7 in other organisms are indicated by dots below the alignment. (B) ClustalX alignment of catalytic C54 domain of Atg4 starting with Asp223 to Lys466 of the S. macrospora ATG4. Following sequences were utilized in the alignment: S.m., F7VV83; N.c., Q7S3X7; P.a., Q86ZL5; M.o., Q523C3; A.n., Q5B7L0; A.o., Q2U5B0; S.c., P53867. The conserved Cys, Asp and His residues of the catalytic triad of the C54 domain are marked with dots under the alignment. Identical amino acids, which are conserved in all proteins, are shaded in black; residues conserved in at least 6 of 7 sequences are shaded in dark gray and residues conserved in at least four sequences are shaded in light gray. Amino acid identity in % is given at the right margin.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.