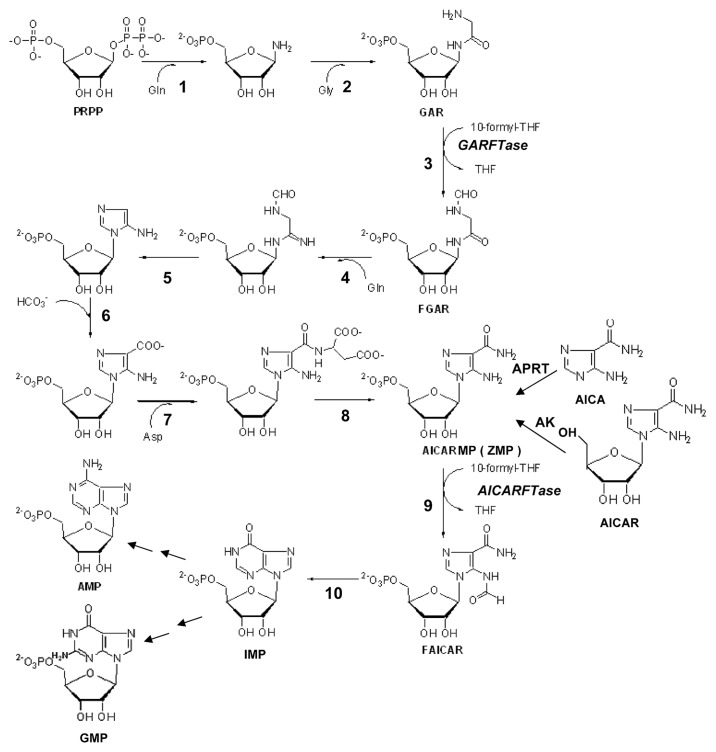
Figure 6. De novo purine nucleotide biosynthesis pathway. The de novo purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway from phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to IMP is shown. The numbered reactions are catalyzed by the following monofunctional enzymes: 1, glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase (GPAT); 4, formylglycinamide ribonucleotide synthase (FGAM synthetase); and 8, adenylosuccinate lyase (ASL). Reactions 2, 3 and 5 are catalyzed by the trifunctional glycinamide ribonucleotide (GAR) formyltransferase (GARFTase) which contains GAR synthase (GARS; reaction 2), GAR formyltransferase (GARFTase; reaction 3) and 5-amino-4-imidazole ribonucleotide synthase (AIRS; reaction 5) activities. Reactions 6 and 7 are catalyzed by the bifunctional phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase/ phosphoribosylaminoimidazole succinocarboxamide synthetase (PAICS) enzyme, which contains carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide synthase (CAIRS; reaction 6) and 5-aminoimidazole-4-(N-succinylocarboxamide) ribonucleotide synthase (SAICARS; reaction 7) activities. Reactions 9 and 10 are catalyzed by a bifunctional enzyme, 5-amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) formyltransferase (AICARFTase)/IMP cyclohydrolase (ATIC) that sequentially catalyzes the last two steps in the pathway for de novo synthesis of IMP. Folate-dependent reactions (reactions 3 and 9) in which 10-CHO-THF serves as the one-carbon donor are catalyzed by GARFTase and AICARFTase. 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide (AICA) and AICAR can be metabolized to AICAR monophosphate (ZMP) by adenine phosphoribosyl transferase (APRT) and adenosine kinase (AK), respectively, thus circumventing the reaction catalyzed by GARFTase.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.