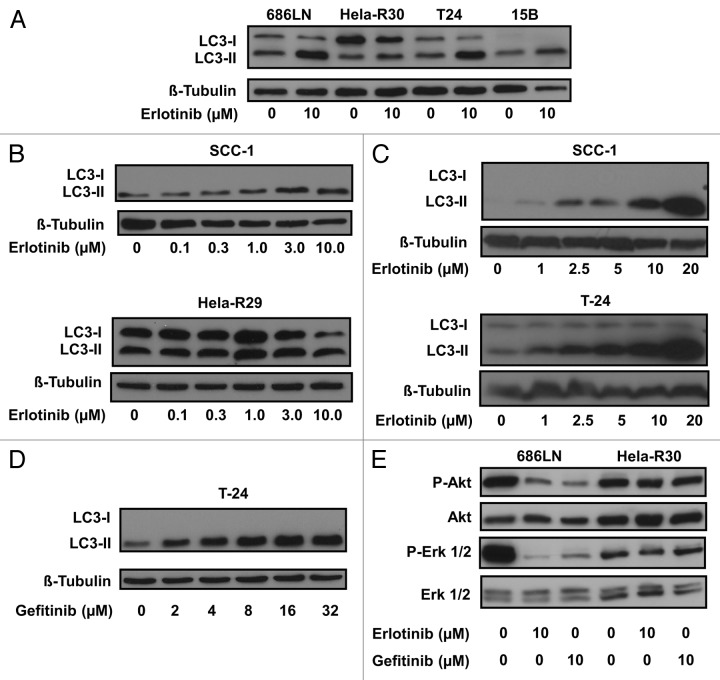
Figure 1. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition induces LC3 lipidation. (A) 686LN, HeLa-R30, T24 and PCI-15B cells were treated with 10 μM erlotinib or carrier control for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting for LC3 and β-tubulin. Erlotinib treatment induces the accumulation of faster migrating phosphatidylethanolamine conjugated LC3 (LC3-II). (B) SCC-1 and HeLa-R29 were treated with erlotinib doses ranging from 0.1 to 10.0 μM for 24 h. A dose-dependent increase in LC3-II was observed in SCC-1 cells but not HeLa-R29 (or R30) cells. (C) SCC-1 and T-24 cells were treated with erlotinib doses in the micromolar (2.5–20 μM) range for 24 h. Dose-dependent increases in LC3-II were observed in both SCC-1 and T-24 cells. (D) T-24 cells treated with gefitinib in the micromolar (2–32 μM) range for 24 h also induce a dose-dependent increase in LC3-II accumulation. (E) Treatment with 10 μM erlotinib or 10 μM gefitinib inhibit Akt and Erk phosphorylation in 686LN but not HeLa-R30 cells. For all immunoblots, image shown is representative of three experimental replicates.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.