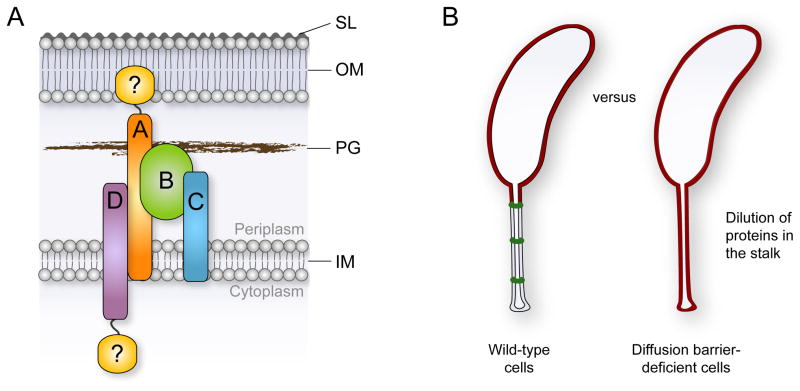
Figure 7. Model for diffusion barrier formation and function.
(A) Diffusion barrier assembly can be envisioned as a nucleation-like process in which StpA (orange) and StpB (green) form the basic scaffold. StpC (blue) and StpD (purple) are accessory components that are required to seal the diffusion barrier. Potential unidentified components of the complex that may establish a connection to the outer membrane or assemble at the cytoplasmic face of the inner membrane are depicted in yellow.
(B) The synthesis of diffusion barriers minimizes the effective volume of the periplasmic space and reduces the physiologically active membrane surface area. In the absence of diffusion barriers, newly synthesized proteins that are targeted to the cell envelope are constantly diluted due to diffusion into the stalk extension.