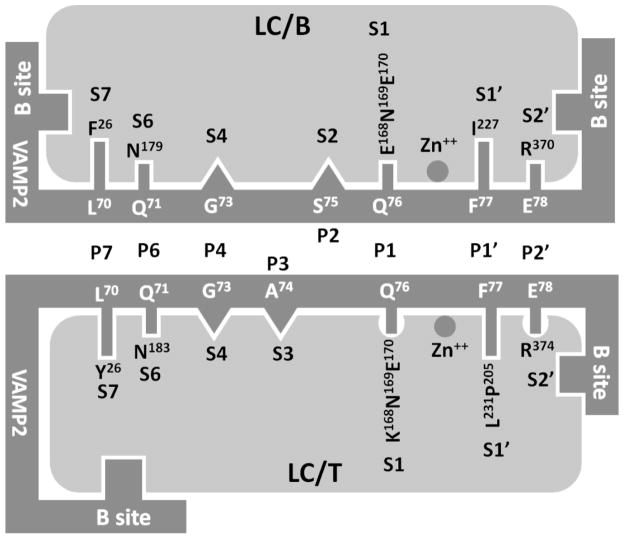
Fig 2. Similarity and difference of substrate recognition by LC/B and LC/T.
The active site substrate recognition for LC/B includes the direct recognition of P7, P6, P1, P1′, and P2′ sites of VAMP2 by the corresponding S pockets in LC/B and the fine alignment of P4 and P3 sites to the S4 and S3 pockets, while the substrate recognition for LC/T includes the direct recognition of P7, P6, P1, P1′, and P2′ sites of VAMP2 by the corresponding S pockets in LC/T and the fine alignment of P4 and P2 sites to the S4 and S2 pockets. The less optimal composition of S1 pocket of and the more complex interaction between P2′-S2′ interaction in LC/T may contribute to the lower kcat of LC/T on VAMP2.