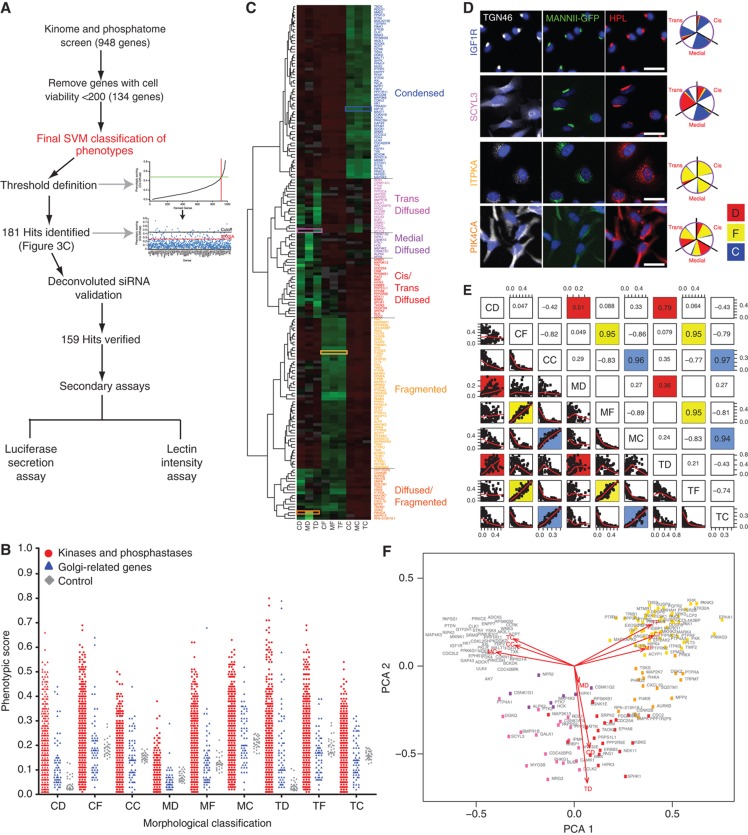
Figure 3.
A large proportion of signaling genes regulate Golgi structure. (A) Schematic workflow of the signaling genes screen. Gene knockdowns having a total cell number of <200 were excluded from the final SVM classification. Thresholds for primary hit identification were defined using the derivative method for each of the nine phenotypic features. Hits were re-tested with the four individual siRNAs present in the pool (deconvoluted siRNA) that was used in the screen (see Supplementary Figure S4A), resulting in 159 validated hits, which were further screened for glycosylation (lectin intensity assay; Figure 8) and secretion (Met-luc secretion assay; Figure 7) changes. (B) Phenotypic scores of signaling genes (red) compared with membrane trafficking genes (blue) and control wells (gray). (C) Clustering of 181 hits using the nine phenotypic features. The range of phenotypic scores is represented by green (high score) to red (low score) in the heatmap. Six major morphological groups were identified and color-coded: condensed (blue), trans diffuse (pink), medial diffuse (purple), cis and trans diffuse (red), fragmented (yellow), diffuse and fragmented (orange). Enlarged version can be viewed in Supplementary Figure S4C. (D) Corresponding images of the genes highlighted in colored rectangles in (C). IGF1R depletion (blue) results in all Golgi compartments condensed; SCYL3 (pink) in strongly diffuse trans compartment; ITPKA (yellow) in all Golgi compartments fragmented; PIK4CA (orange) in a mix of diffuse and fragmented for all compartments. Scale bar: 30 μm. (E) Correlation plots of the nine phenotypic features. CD, MD, TD, CF, MF, TF, CC, MC and TC refer to cis diffuse, medial diffuse, trans diffuse, cis fragmented, medial fragmented, trans fragmented, cis condensed, medial condensed, and trans condensed, respectively. (F) Principal component analysis (PCA) of the nine phenotypic features. Color coding corresponds to the six morphological groups defined in (C).