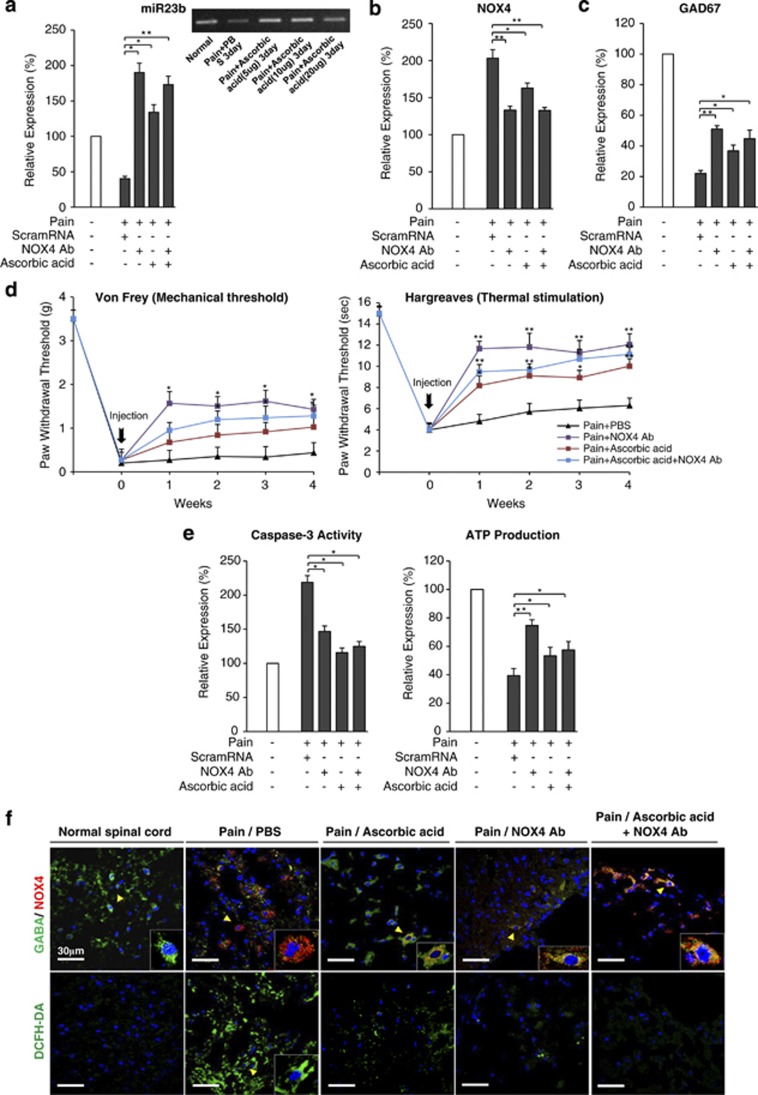
Figure 4.
Functional amelioration efficacy of NOX4 antibody treatment after infusion. (a) The expression level of miR23b was determined by RT-PCR after injection of different dosages of ascorbic acid: 5, 10, and 20 μg. The expression level of miR23b was significantly increased by both the 5 and 10 μg dosages of ascorbic acid. The graph shows that the expression level of miR23b was increased after injection of NOX4 antibody (Ab) and ascorbic acid+NOX4 Ab. The miR23b expression level in the NOX4 Ab-treated group was significantly increased compared with other two groups (*P<0.05; **P<0.01). (b) The expression level of NOX4 was significantly decreased after injection of NOX4 Ab, ascorbic acid, or ascorbic acid+NOX4 Ab (*P<0.05; **P<0.01). (c) The expression level of GAD67 was significantly increased after injection of NOX4 Ab, ascorbic acid, or ascorbic acid+NOX4 Ab. GAD67 expression in the NOX4 Ab-treated group was significantly increased compared with other two groups (*P<0.05; **P<0.01). (d) PWTs were determined using von Frey filaments to measure hypersensitivity. At 1 week after injection of NOX4 Ab, ascorbic acid, or ascorbic acid+NOX4 Ab, hypersensitivity was significantly decreased. PWTs were maintained for 4 weeks with similar patterns as the first week. The Hargreaves method was used to measure responses to noxious thermal stimulation. The Hargreaves test showed a significant decrease 1 week after injection that was maintained for 4 weeks. The results were similar in pattern to those of the von Frey test (*P<0.05; **P<0.01). (e) ATP production and caspase-3 activity were determined after injection of NOX4 Ab, ascorbic acid, and ascorbic acid+NOX4 Ab. Caspase-3 activity was significantly decreased by injection of NOX4 Ab, ascorbic acid, or ascorbic acid+NOX4 Ab. ATP production was significantly increased after the injection of NOX4 Ab compared with the injured animal model. The ascorbic acid and ascorbic acid+NOX4 Ab groups showed increased ATP production. However, efficacy of ATP production was lower than the NOX4 Ab-treated group. (f) The colocalization expression levels of NOX4 (red) and GABA (green) were analyzed and compared with the pain/PBS, pain/ascorbic acid, pain/NOX4 Ab, and pain/ascorbic acid+NOX4 Ab models using confocal microscopy (arrow). The expression level of NOX4 was predominantly decreased compared to animals with neuropathic pain after injection of NOX4 Ab, ascorbic acid, or ascorbic acid+NOX4 antibody. ROS production was determined using DCFH-DA (green). ROS production was significantly increased after injury or pain/PBS, whereas it was predominantly decreased after injection of NOX4 Ab, ascorbic acid, or ascorbic acid+NOX4 Ab. Inset shows colocalization at the single-cell level