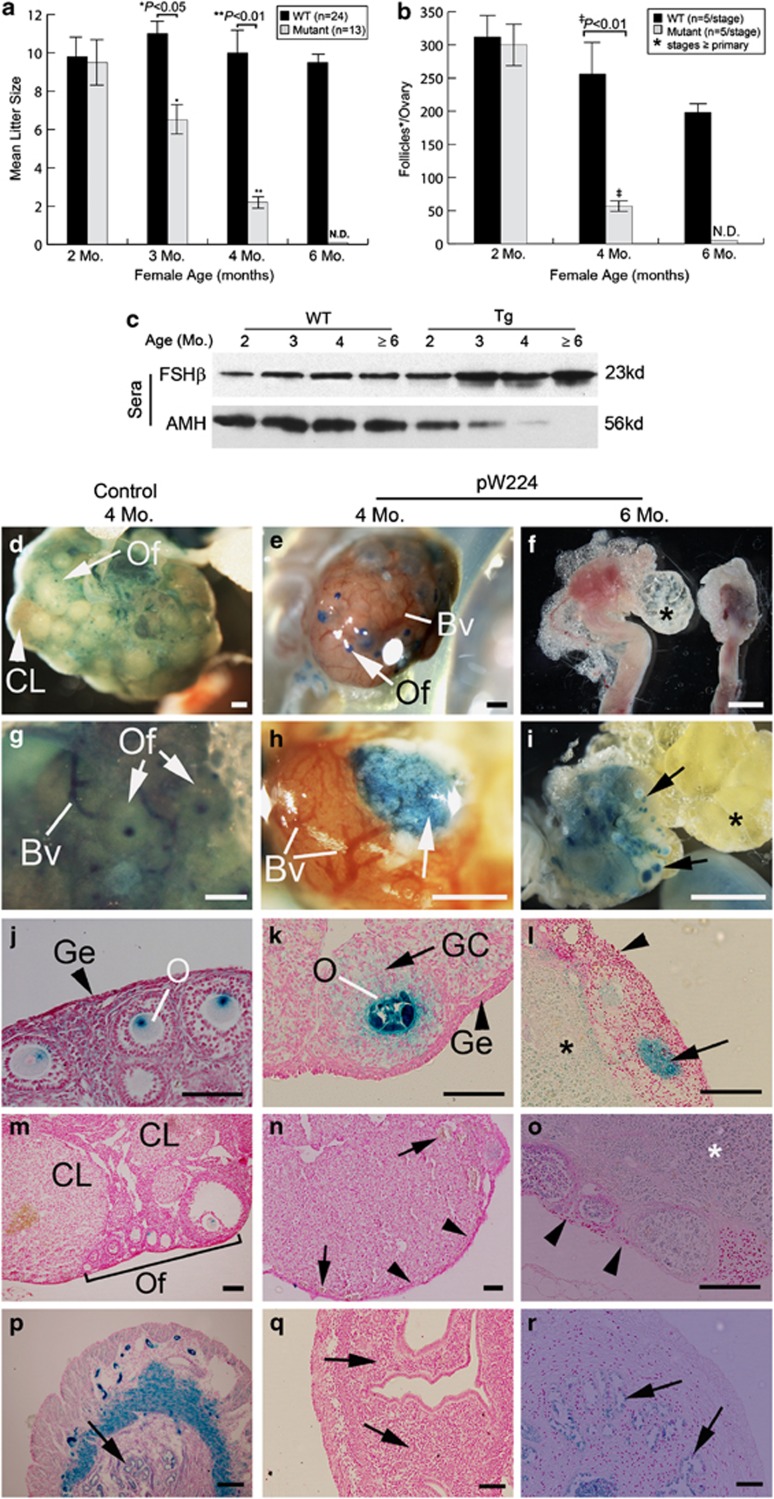
Figure 5.
Multiple reproductive defects in the Umodl1-Tg females. Accelerated decline in litter size (a) and number of maturing follicles per ovary (b) were observed in the Tg females. Error bars indicate S.D. Litter size and follicle number between WT and Tg mice at specified age were compared using Student's t-test. Genotypes and sample size are indicated in the upper right corners of panels a and b. N.D., not detectable. (c) Western blot assay to examine the dynamics of serum FSHβ and AMH levels as the WT and Tg females aged. Genotype and sample age are indicated on the top. (d–r) Histological analysis showing the progression of ovarian degeneration. A 4-month-old Lycat-BAC Tg ovary was included as the healthy control (panels in the left column). (d–i) whole mount views of freshly isolated (f) or lacZ-stained (d, e, g, h and i) ovaries from the control and ageing pW224 mice. Panels g and h are the higher power views of panels d and e, respectively. Panel i shows the left ovary in panel f at a higher magnification after lacZ-staining. Panels j–o are sectioned control (j and m) and mutant (k, i, n and o) ovaries. Panel m is a representative photograph showing all types of ovarian cells, including CL, interstitial stromal cells, and follicles of various stages (of primordial, primary, secondary & pre-ovulatory follicles). The arrows in panel i show the degenerated follicles filled with lipid droplets. The arrowheads in panels l and o indicate the absence of germinal epithelial layer in a 6-month-old ovary. The arrow in panel l indicates a degenerated follicle devoid of oocyte. Arrowheads in panel n show the absence of primordial ovarian follicles in the cortex region. Arrows in panel n indicate abnormal blood vessel formation in the Tg ovary. Higher power views of the regions specified by arrows and arrowheads in panel n can be found in Supplementary Figures 1f–h. Regions marked by asterisks in Panels l and o are the ovarian medulla that has become nuclear-fast-red negative. Secondary to the ovarian defects, progressive abnormalities can be seen in the mutant uteri (p–r). Arrows in panels p–r specify the uterine glandular epithelial cells. Genotype and age are indicated on the top of each column. Scale bar in sections, 100 μm