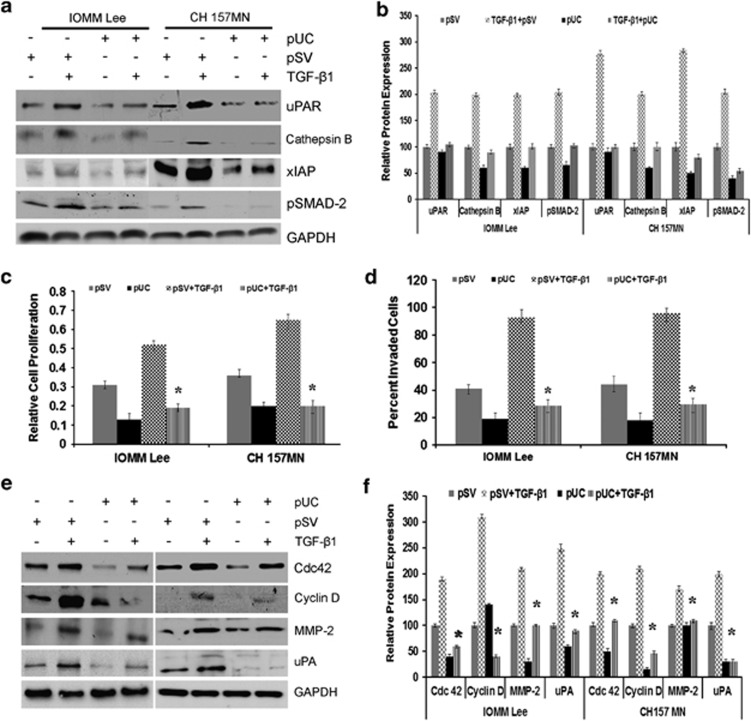
Figure 5.
Downregulation of uPAR and cathepsin B decreases TGF-β1-induced proliferation and invasion in meningioma. (a) Cells (1.5 × 105) seeded in a six-well plate were transfected with scrambled vector (pSV) or pUC for 24 h and stimulated with TGF-β1 for another 24 h. Cell lysates were probed for uPAR, cathepsin B, XIAP, and pSMAD-2; GAPDH served as a loading control. Each blot is representative of three independent experiments. (b) The band intensities from each blot were quantified with ImageJ software and relative expression levels were plotted. Columns: mean; bars: ±S.D.; n=3. (c) Treated cells were analyzed for cell proliferation after another 48 h and relative cell proliferation was plotted. Columns: mean; bars: ±S.D.; n=3; *P<0.05 versus control. (d) After 24 h of TGF-β1 treatment, cells were allowed to invade Matrigel-coated transwell inserts for further 24 h at 37 °C before fixing and staining. Then, the invaded cells were photographed under a light microscope and the percent invaded cells were plotted. Columns: mean; bars: ±S.D.; n=3; *P<0.05 versus control. (e) Lysates from pSV- and pUC-treated cells were probed for Cdc42, cyclin-D, MMP-2, and uPA; GAPDH served as a loading control. Each blot is representative of three independent experiments. (f) The band intensities from each blot were quantified with ImageJ software and relative expression levels were plotted. Each column designates mean±S.D. of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, significant difference from SV+TGF-β