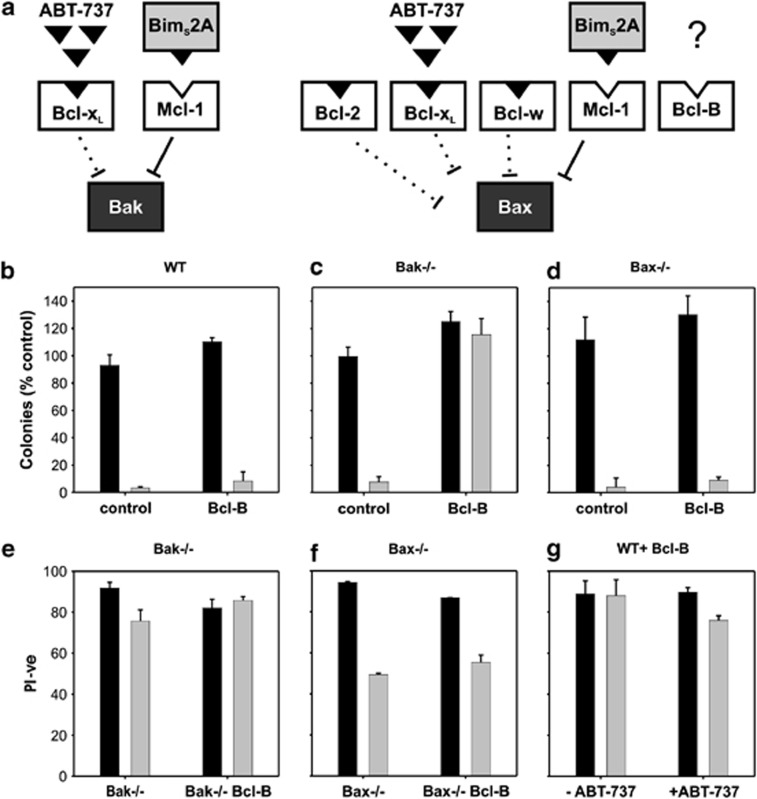
Figure 5.
Bcl-B inhibits Bax- but not Bak-initiated apoptosis. (a) Schematic diagram of experiments directed towards determining the Bax or Bak specificity of Bcl-B in the presence of other prosurvival proteins. Neutralization of Bcl-xL, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w is achieved with the drug ABT-737, whereas Mcl-1 is neutralized using a specific inhibitor, BimS2A. Bcl-B binds neither of these inhibitors and its ability to inhibit either Bax- or Bak-initiated apoptosis in the presence of other prosurvival proteins can be determined. (b) Expression of Bcl-B in wild-type (WT) MEF cells does not prevent cell death upon inactivation of endogenous prosurvival proteins Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, Bcl-w and Mcl-1. WT MEFs stably expressing Bcl-B were infected with BimS2A or the inactive BimS4E retrovirus, and then treated for 24 h with 1 μM ABT-737. Colonies were counted after 7 days and expressed as a percentage of control (BimS4E) infected cells. (c) and (d) Bcl-B is able to restrain Bax but not Bak activation. Bak−/− and Bax−/− MEFs stably expressing Bcl-B were infected with BimS2A or the inactive BimS4E retrovirus, and then treated for 24 h with 1 μM ABT-737. Viability was measured by propidium iodide (PI) exclusion (e–g) and expressed as the percentage of control (BimS4E). Long-term survival was measured by following colony formation 7 days after ABT-737 treatment. BimS4E- and BimS2A-infected cells are shown in dark and light bars, respectively