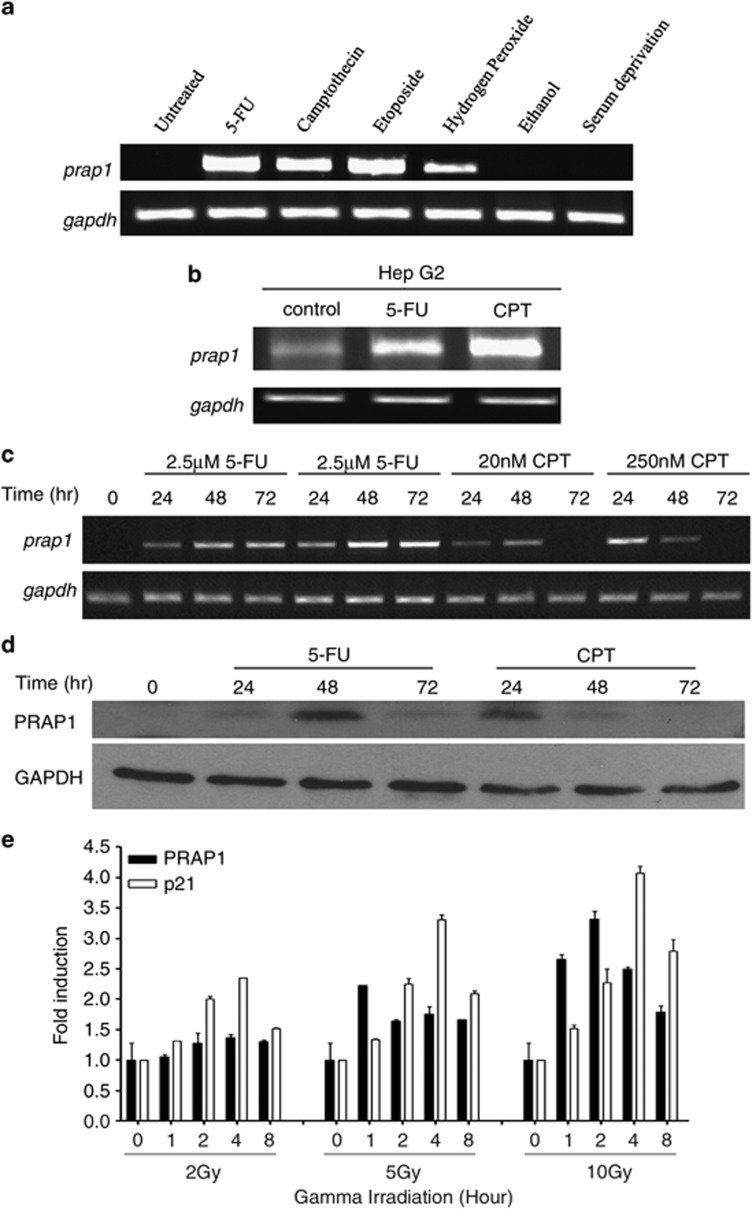
Figure 1.
PRAP1 is induced by DNA-damaging agents. (a) PRAP1 mRNA is induced by DNA-damaging agents in HCT116 cells. Reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR gel picture showing the expression of prap1 and gapdh (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) in HCT116 cells after treatment with the indicated stressors 5-FU (25 μM), CPT (20 nM), etoposide (20 μM), 5% ethanol or serum-free medium for 48 h; hydrogen peroxide (100 μM) for 1 h and recovered for 4 h. With the exception of ethanol and serum deprivation, PRAP1 mRNA expression was induced by all the other agents. (b) PRAP1 mRNA is induced by DNA-damaging agents in HepG2 cells. RT-PCR gel picture showing the increased expression of prap1 and gapdh in HepG2 cells after treatment with 5-FU (25 μM) and CPT (20 nM) for 48 h. (c) PRAP1 mRNA is induced by DNA-damaging agents in a dose-dependent manner. RT-PCR gel picture showing the enhanced expression of prap1 and gapdh in HCT116 cells after treatment with 5-FU and CPT at the indicated doses for 24, 48 and 72 h. (d) PRAP1 protein is induced by DNA-damaging agents in a time-dependent manner. Western blot showing the expression of PRAP1 and GAPDH in HCT116 cells after treatment with 5-FU (25 μM) and CPT (20 nM) for 24, 48 and 72 h. (e) PRAP1 and p21 mRNA are induced by gamma irradiation. Graph shows fold induction of prap1 and p21 expression in HCT116 cells after treatment with gamma irradiation at 2, 5 and 10 Gy and recovered at 1, 2, 4 and 8 h. Real-time RT-PCR was performed and relative expression of prap1 and p21 were normalized against gapdh and calculated as fold induction