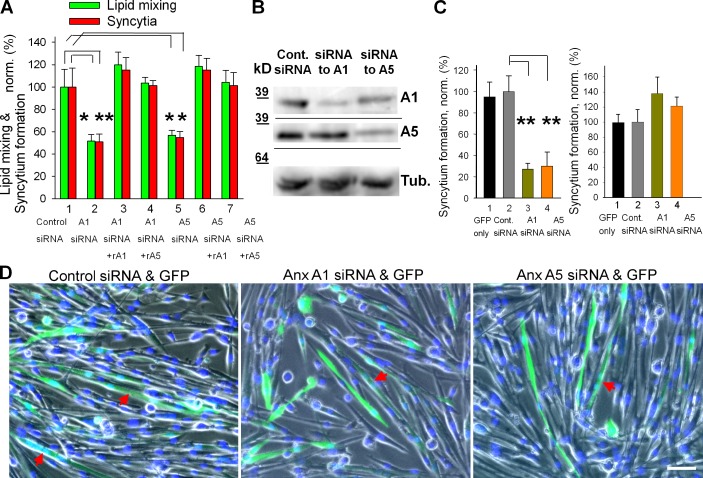
Figure 3.
siRNAs targeting expression of Anx A1 or A5 inhibit fusion of primary myoblasts. (A) Inhibition of lipid mixing (green) and syncytium formation (red) at 24 h in DM by A1 and A5 siRNAs is reversed by application of rA1 or rA5. 1, cells transfected with negative control siRNA; 2–4, cells transfected with A1 siRNA; 5–7, cells transfected with A5 siRNA. rA1 (3 and 6) and rA5 (4 and 7) were applied 3 h before scoring fusion. (B) The cells transfected with control siRNA or A1 or A5 siRNAs were lysed after 24 h in DM and analyzed by Western blot to evaluate levels of expression of Anx A1 and A5 and tubulin (as a loading control). (C) After cotransfection of primary myoblasts with siRNA and GFP vector, we separately assayed syncytium formation for transfected (left) and not-transfected (right) cells. 1, transfection with GFP vector alone; 2, cotransfecion with GFP vector and negative control siRNA (taken as 100%); 3 and 4, cotransfection with GFP vector and siRNA to either Anx A1 (3) or A5 (4). (D) Phase-contrast images with nuclear staining (blue) and GFP fluorescence (green) showing myoblasts cotransfected with GFP and control (left), Anx A1 (middle), or Anx A5 (right) siRNA. Arrows mark the GFP-labeled multinucleated cells. Bar, 50 µm. (A and C) All results are shown as means ± SEM (n ≥ 3). Levels of significance relative to controls (1 in A and 2 in C) are shown: **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.