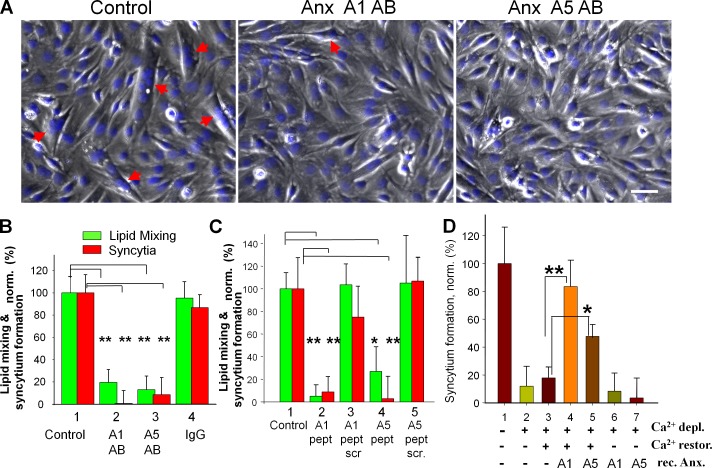
Figure 5.
Synchronized fusion of C2C12 cells is influenced by reagents targeting extracellular Anx A1 and A5. (A) Phase-contrast images with nuclear staining (blue) showing C2C12 cells that were incubated in DM for 51 h and then in LPC-supplemented DM for 16 h, and, finally, placed into LPC-free DM (left) or LPC-free DM with antibodies to Anx A1 or A5 (middle and right). The images were taken 30 min after LPC removal. Arrows mark the multinucleated cells. Bar, 50 µm. (B–D) Antibodies (B), A1- and A5-peptides (C), and EGTA (D) were applied to ready-to-fuse myoblasts at the time of LPC removal (B and C) or 30 min before LPC removal (D). Fusion was scored 30 (B and C) or 60 (D) min after LPC removal and normalized to fusion in the control experiments shown (B–D, 1). (B) Lipid mixing (green) and syncytium formation (red) were inhibited by antibodies to Anx A1 (2) and A5 (3) but not by nonspecific IgG (4). 1, untreated cells released from LPC block. (C) Fusion was inhibited by the peptides to Anx A1 (2) and A5 (4) but not by their scrambled versions (3 and 5). (D) At the time of LPC removal, the cells were placed into Ca2+- and Mg2+-free LPC-free PBS supplemented with 10 mM EGTA (2–7). (3–5) 30 min after LPC removal, we washed the cells with EGTA-free Ca2+- and Mg2+-containing PBS (3) or with the same buffer supplemented with rA1 (4) or rA5 (5). (6 and 7) As in 4 and 5, but rA1 (6) and rA5 (7) were applied in Ca2+- and Mg2+-free PBS. (1) At the time of LPC removal, the cells were placed into Ca2+- and Mg2+-containing PBS. All results are means ± SEM (n ≥ 3). (B–D) Levels of significance relative to 1 in B and C and to 3 in D are shown: **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.