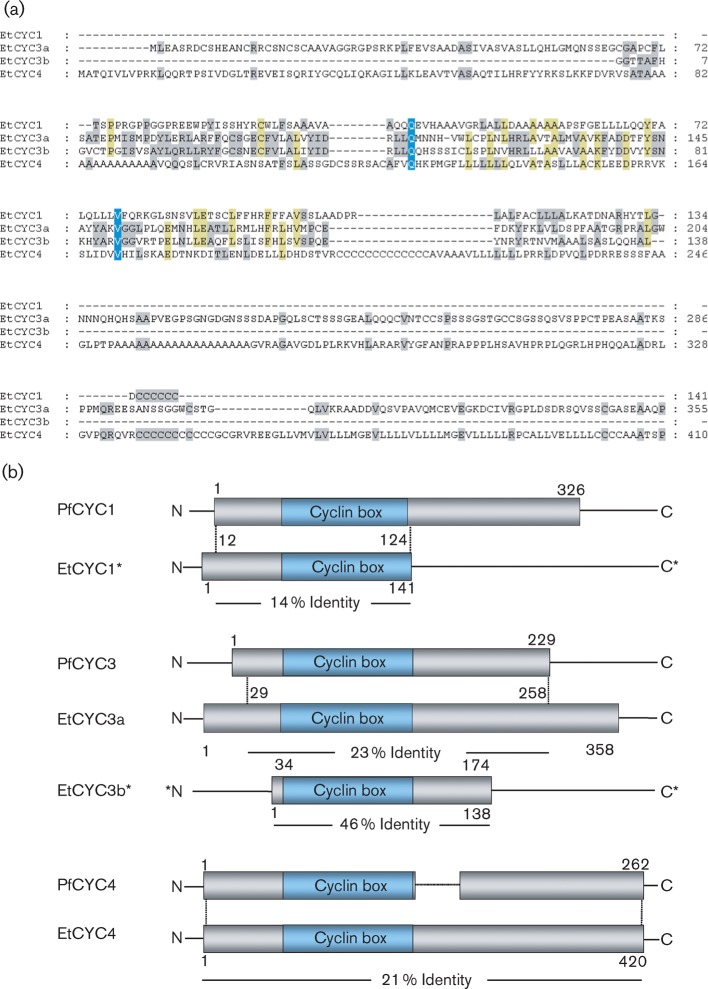
Fig. 1.
Bioinformatic identification of cyclin-like proteins of E. tenella. (a) Multiple sequence alignment of the potential cyclin-like E. tenella proteins (EtCYC1, EtCYC3a, EtCYC3b and EtCYC4). For EtCYC1 and EtCYC3b, only incomplete sequences could be identified. Blue-shaded residues are conserved among the four sequences, yellow-shaded residues among any three of the four sequences, grey-shaded residues among any two only. (b) Comparison of known cyclin-like sequences of P. falciparum and E. tenella. The potential cyclin-like proteins are homologous to the known cyclin-like proteins of P. falciparum. The characteristic cyclin box sequence motif is conserved among the apicomplexan cyclin-like protein sequences and is coloured blue.