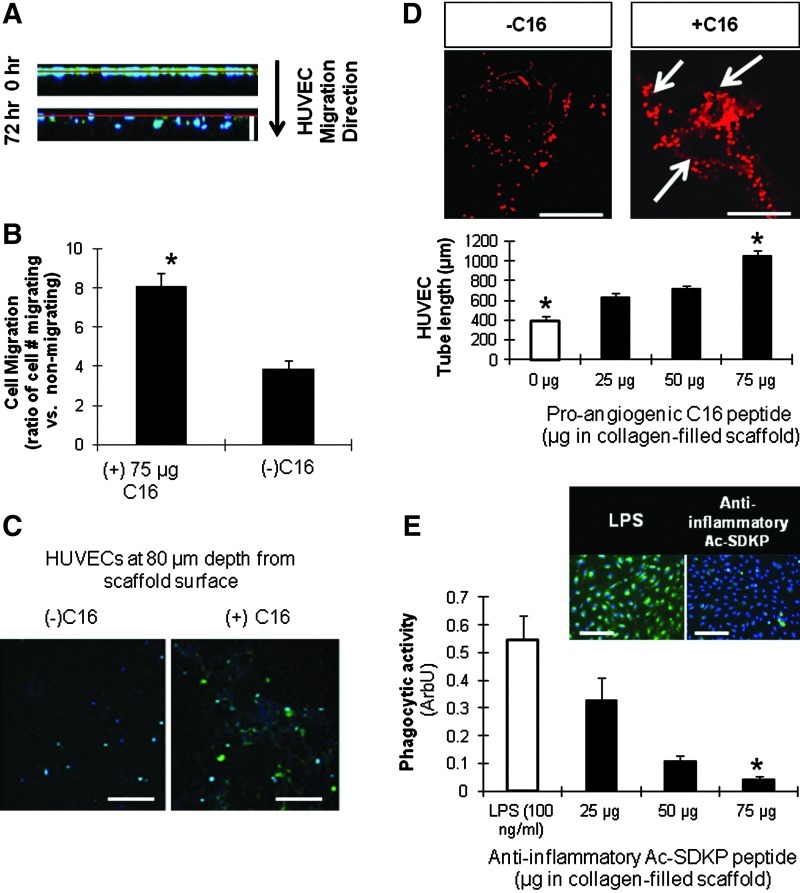
FIG. 3.
Peptide characterization. (A, B) Human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) migration into scaffolds. Cell nuclei (blue) and proliferating cells with BrdU incorporation (green). (A) Z-sectional projection of HUVEC migration from the surface (red line). White scale bar: 120 μm. (B) Effect of C16 peptide (75 μg/scaffold) on HUVEC migration at 72 h. Ratio of migrated versus nonmigrated HUVECs was defined as the number of cells migrated a distance >0 μm into the scaffolds divided by the number of cells remaining at the surface. (C) Representative images of HUVECs that have migrated 80 μm into the scaffold after 72 h. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Tubulogenesis (as measured by total tube length) of HUVECs around 40 μm into the scaffold in response to varying doses of pro-angiogenic C16 peptide. Ethidium bromide stained HUVECs with (right) and without (right) C16 shown in top images. White arrows indicate points of tube formation. Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) MDM phagocytic activity. Macrophages (blue) and phagocytized Escherichia coli particles (green) shown in the top images. The phagocytic activity presented by the green fluorescence intensity normalized to cell number in the bottom graph. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B, D, E) *p<0.05 versus all the other conditions in same graph (n=5). MDM, monocyte-derived macrophage. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea