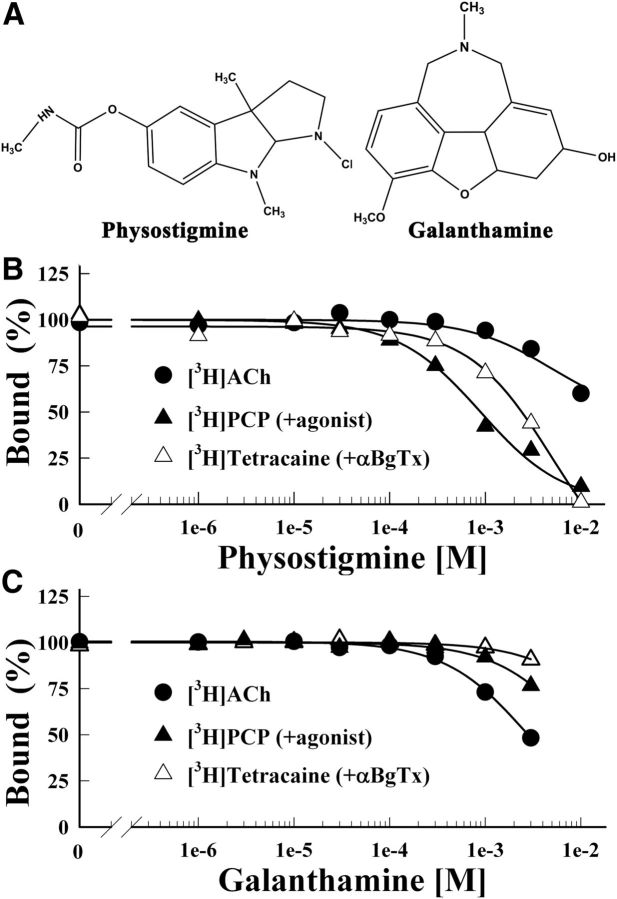
Figure 1.
Physostigmine and galanthamine inhibition of the equilibrium binding of [3H]ACh, [3H]tetracaine, and [3H]PCP to the Torpedo nAChR. A, The chemical structures of physostigmine and galanthamine. B, C, The equilibrium binding of [3H]ACh (●), [3H]tetracaine (+α-BgTx, ▵), or [3H]PCP (+Carb, ▴) was determined using centrifugation assays in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of physostigmine (B) or galanthamine (C). For each competition experiment, the data were normalized to the specific binding in the absence of competitor. Total binding for [3H]ACh was 1313 ± 5 cpm, with 88 ± 10 cpm nonspecific (+ 1 mm Carb); for [3H]tetracaine, 24,400 ± 120 cpm, with 5583 ± 16 cpm nonspecific (+ 100 μm tetracaine); for [3H]PCP, 6854 ± 52 cpm, with 437 ± 6 cpm nonspecific (+ 100 μm Proadifen). Physostigmine inhibited [3H]tetracaine and [3H]PCP binding with IC50s of 5 ± 1 mm and 0.9 ± 0.1 mm, respectively. Galanthamine inhibited [3H]ACh binding with IC50 = 2.8 ± 0.1 mm.