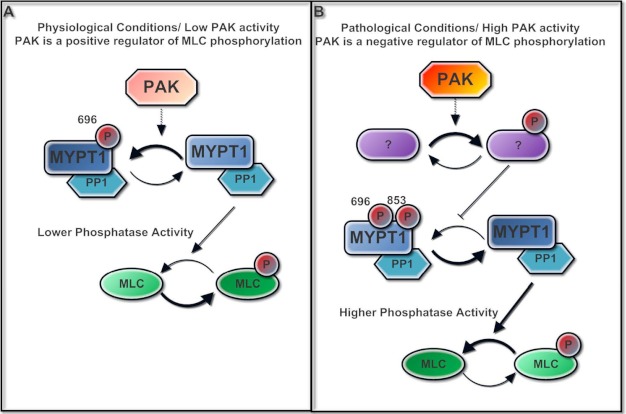
FIGURE 9.
Theoretical model of the dual function of PAK in regulating intestinal smooth muscle myosin light chain phosphorylation. A, under physiologic conditions, PAK positively regulates MLC phosphorylation through phosphorylation of MYPT1 at the Thr-696 site. B, under pathologic conditions, overstimulated PAK switches its signaling to a different pathway, which negatively regulates MLC phosphorylation via decreased MYPT1 phosphorylation at both the Thr-696 and Thr-853 sites.