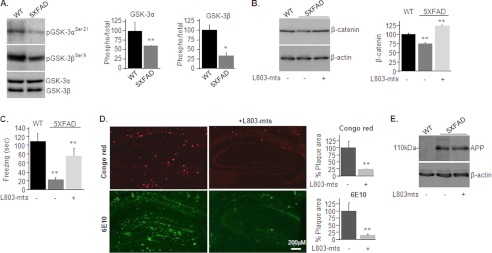
FIGURE 1.
L803-mts reduces Aβ plaque loads and improves cognitive performance in the 5XFAD mouse model. A, phosphorylation and expression levels of GSK-3α/β in brain samples of WT and 5XFAD mice as determined by immunoblot analysis. B, β-catenin levels in brain samples from WT and L803-mts-treated or nontreated 5XFAD mice as determined by immunoblot analysis. Densitometry analyses of indicated bands or calculated ratios are shown on the right for each panel. C, freezing time duration determined in WT mice and in L803-mts-treated or nontreated 5XFAD mice, as evaluated in the contextual fear conditioning test. D, representative histological images of paraformaldehyde-fixed hemi-brain sections obtained from L803-mts-treated or nontreated 5XFAD mice. The upper panels show a Congo red stain, and the lower panels show an immunostaining using anti-Aβ antibody (6E10). The percentage of plaque load area is shown on the right. E, expression levels of APP in brain samples from WT and L803-mts-treated or nontreated 5XFAD mice as determined by immunoblot analysis. Densitometry analyses for all panels are the means ± S.E. of five or six animals. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005. Equal protein loads were verified by β-actin blots (B and E).