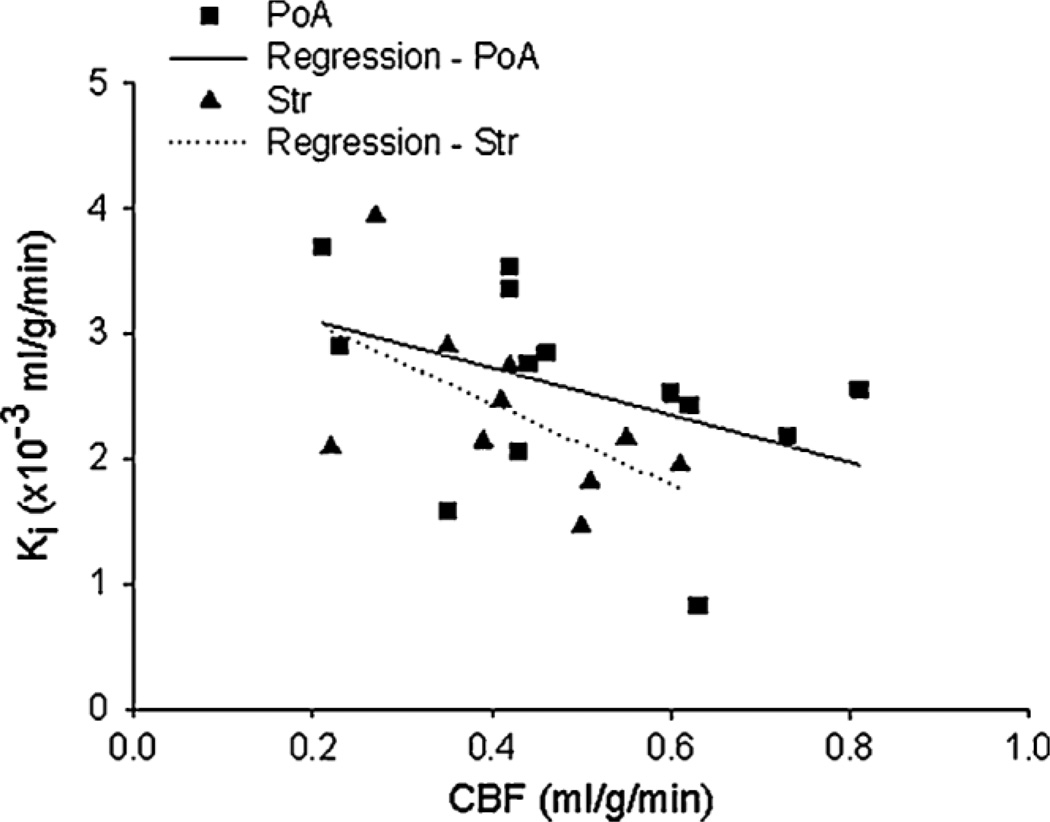
Figure 4.
A scatter plot of the influx rate constants (Ki) vs cerebral blood flow (CBF) measured during the period of middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion for 23 regions of interest within the preoptic area (PoA) and striatum (Str). Separate regression lines are drawn for the PoA and Str data. An apparent inverse relationship was observed between the two measurements, suggesting that the extent of CBF reduction during occlusion may be a factor contributing to later blood–brain barrier (BBB) damage. That is, BBB opening tended to be highest in regions of interest with the lowest rates of flow during occlusion and lowest in those with the highest rates. Statistical analysis, however, did not support this suggestion.