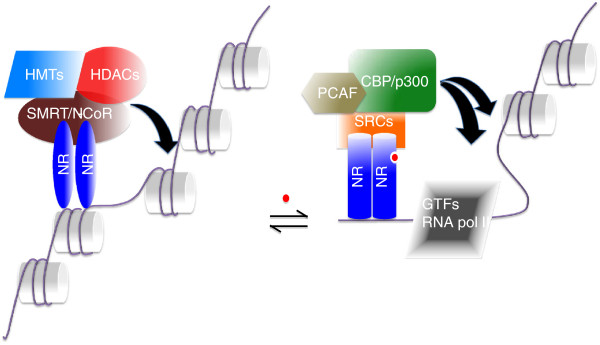
Figure 2.
Ligand-dependent conformational change and transactivation of a nuclear receptor. In the absence of ligand, nuclear receptors are associated with corepressor complexes such as SMRT, HDACs and histone methyltransferases (HMTs) and inhibit transcription by keeping the chromatin tightly bound around the promoter. Ligand binding induces a conformational change in the structure of nuclear receptors which exchanges the corepressors with coactivators. The coactivators including CBP/p300, PCAF and SRCs loosen chromatin by acetylating histone tails. Acetylation of histone tails opens up the chromatin which in turn allows basal transcriptional machinery to target promoters.