Fig. 2.
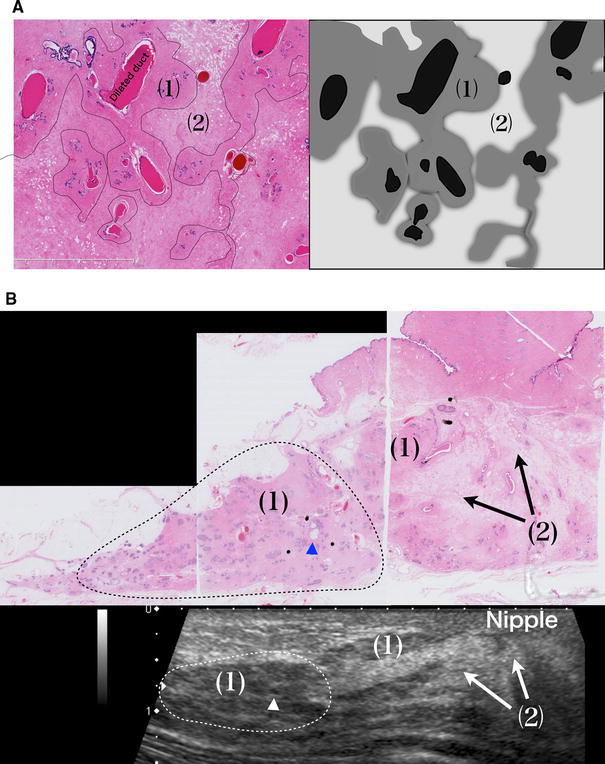
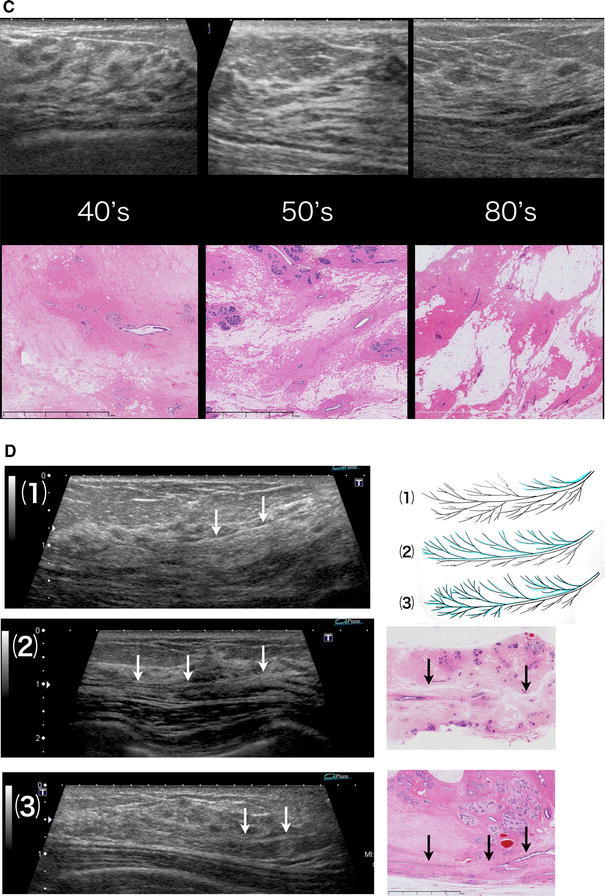
(a) (1) Stroma that is densely packed with fibrous connective tissues and surround the lobules and an extralobular duct (isoechoic). (2) Edematous stroma with loosely packed fibrous connective tissues (hyperechoic). Isoechoic structures can be confirmed by ultrasound (US). The difference in acoustic impedance density between (1) and (2) is visualized as the iso- to hyperechoic area. b (1) Stroma surrounding lobules and ducts = isoechoic. (2) Edematous stroma = hyperechoic. Triangle Microcyst = hypoechoic. Dotted line The area where the lobulus crowds = isoechoic. c Comparison of US and the histology an age change. In stroma with loosely packed fibrous connective tissues, the ratio between edematous stroma and fat varies depending on age and other factors, but they are visualized as hyperechoic areas regardless of the ratio. d Lobes of various sizes overlap each other, causing varied appearance of the boundary surfaces. (1) If the lobe in front is smaller, the boundary surface is visible in the shallow area. (2) If the lobes in the front and back are of comparable size or the lobe in front is slightly larger, the boundary surface is widely visible to the terminal area. (3) If the lobe in front is larger and the lobe in back is smaller, the boundary surface is visible in the deep area
