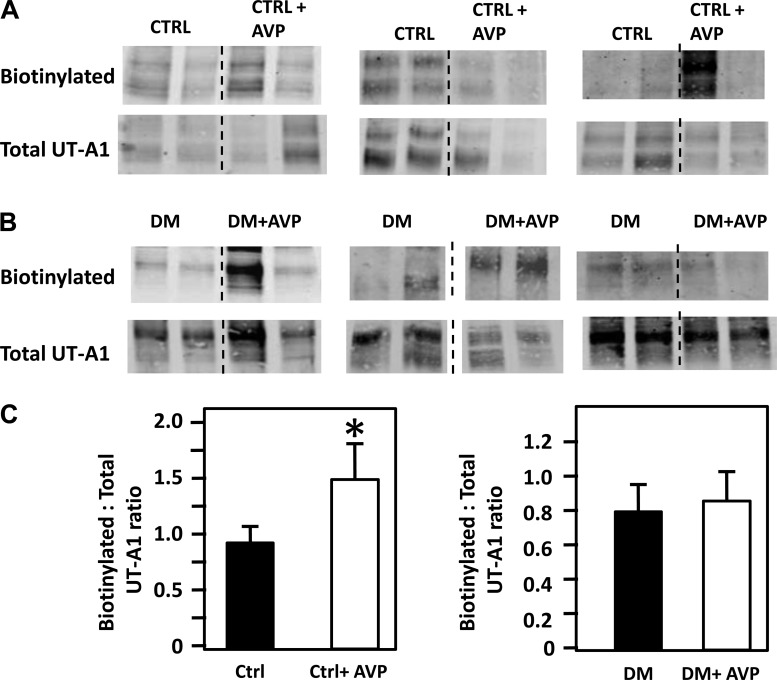
Fig. 5.
Vasopressin (AVP) increases apical membrane accumulation of UT-A1 in inner medullary collecting ducts (IMCDs) from nondiabetic control rats (A) but not diabetic (DM) rats (B). A: top, Western blot showing the membrane-bound UT-A1 (biotinylated) in nondiabetic control (CTRL) rat IMCD suspensions, with and without AVP treatment. Immediately below is the Western blot showing total UT-A1. B: top, Western blot showing the membrane-bound UT-A1 in diabetic rat IMCD suspensions, with and without AVP treatment. Immediately below is the Western blot showing total UT-A1 in diabetic rats. Western blots include representative Western blot protein bands from three of the four experiments in which we looked at the biotinylation of UT-A1 under these conditions. C: left, bar graph showing the amount of biotinylated UT-A1 per unit of total protein in control animals with and without AVP, combining the results from four different experiments (n = 8–13, P < 0.05). Right, bar graph showing biotinylated UT-A1 per unit of total protein in diabetic animals treated with and without AVP, combining the results from four different experiments [n = 12–16, P = not significant (NS)]. *P < 0.05.