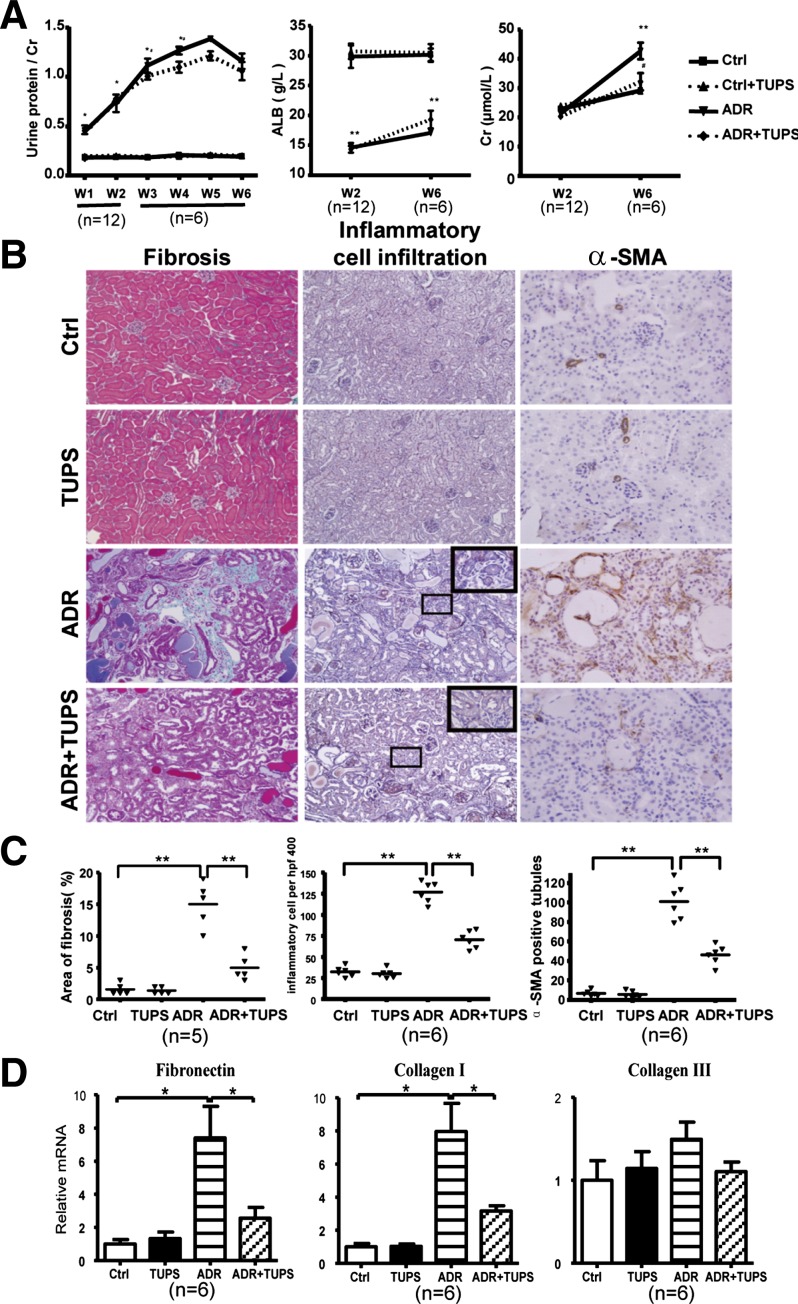
Fig. 5.
sEH inhibition improved parameters in adriamycin (ADR)-induced nephropathy in mice. The ADR-induced nephropathy mouse model was established with tail vein injection of 10 mg/kg of ADR. The animals were divided into 4 groups (at least 6 mice in each group): control (Ctrl), ADR, TUPS, and ADR+TUPS. PBS treatment was a control. For TUPS treatment, sEH inhibitor TUPS (1.0 mg·kg−1·day−1) was given by oral gavage for 2 or 6 wk. A: 24-h urine protein level was determined every week; serum albumin and creatinine levels were measured 2 or 6 wk after ADR administration. B: cross sections of mouse kidneys at 6 wk after ADR injection histochemically stained with Masson (fibrosis), pulmonary artery smooth muscle (inflammation), and α-SMA (×400). C: area of fibrosis, number of inflammatory cells and number of α-SMA positive tubules in the cross-sections were measured. D: real-time RT-PCR quantification of mRNA levels of collagen I, collagen III, and fibronectin, Data are means ± SD of the relative mRNA normalized to that of GAPDH from at least 6 mice in each group (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).