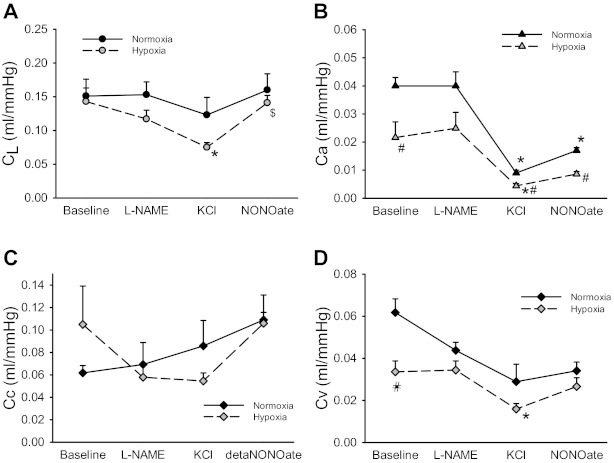
Fig. 1.
Chronic hypoxia (CH) had little effect on the total pulmonary vascular compliance (CL) but resulted in lower arterial compliance (Ca) and venous compliance (Cv). Nitric oxide (NO) resulted in a significant increase in compliance in CH lungs after KCl-induced vasoconstriction. Vascular compliance was estimated from vascular occlusion maneuvers in isolated perfused lungs using a five-compartment model that included CL (A), Ca (B), Cv (C), and microvascular complicance (Cc; D). Vascular occlusions were performed under four conditions, each lasting 30 min: baseline (BL), 3 mM Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME), 30 mM KCl, and 100 μM diethylenetriamine (DETA)-NONOate. *Different from BL in the same group (P < 0.05); $different from 30 mM KCl in the same group (P < 0.05); #CH different from normoxia (N) with the same perfusate (P < 0.05).