Fig. 2.
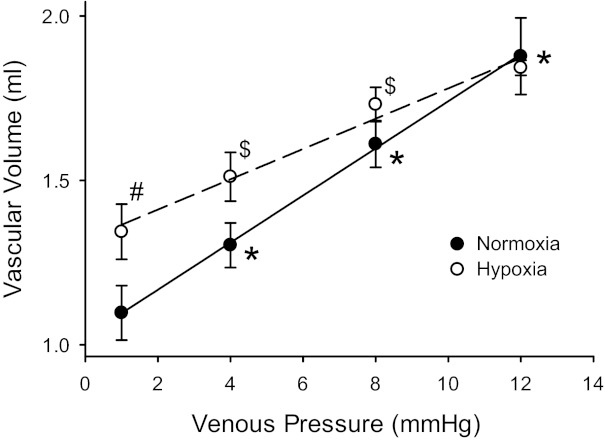
Static vascular compliance was greater in lungs from N rats than in those from CH rats. Vascular volume (QL) was measured by thermodilution at four different venous pressures (Pv) at a constant flow rate of 20 ml/min in isolated lungs from N (n = 7) and CH (n = 6) rats. QL increased in N lungs with each increase in Pv. Although the QL at a Pv of 1 mmHg was greater in CH rats, there was a smaller change in QL for each Pv increase, and the change in Pv from 8 to 12 mmHg did not significantly increase QL. The slopes of the lines (static vascular compliance) were different (P < 0.01) by analysis of covariance (0.070 ± 0.009 ml/mmHg in N vs. 0.046 ± 0.007 ml/mmHg in CH). #CH different from N at the same Pv (P < 0.001); *QL different from previous Pv in N lungs (P < 0.001); $QL different from previous Pv in CH lungs (P < 0.05).