Fig. 1.
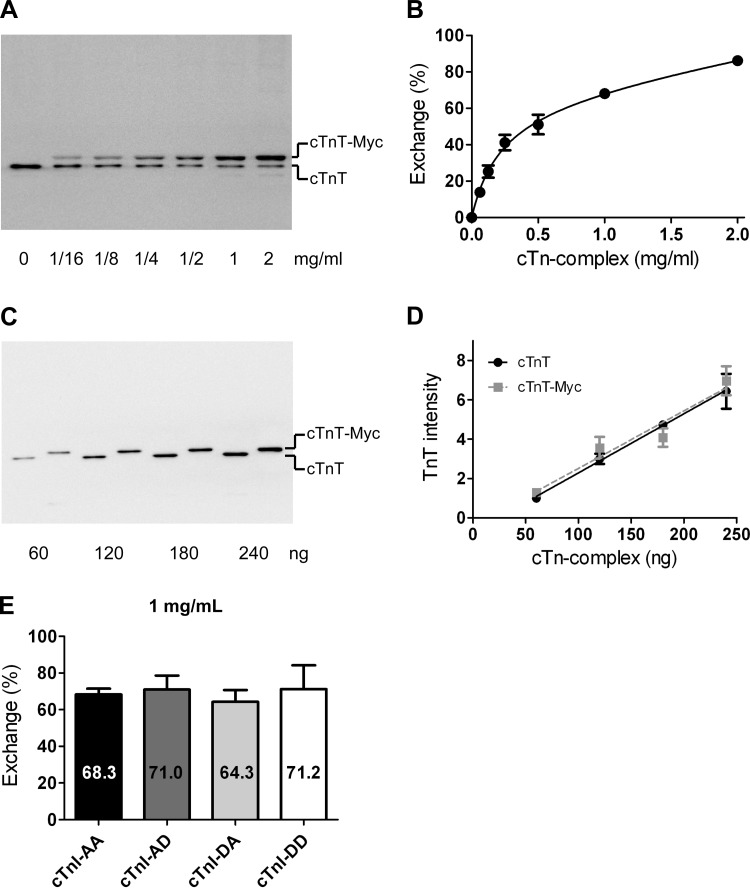
Quantification of troponin exchange in cardiomyocytes by immunoblotting. A: immunoblot stained with an antibody against cardiac troponin (cTn)T that recognizes both endogenous cTnT (bottom band) and recombinant myc tag-labeled cTnT (cTnT-myc; top band). The example shows a suspension of cardiomyocytes exchanged with increasing concentrations of recombinant cTn. B: average percentages of cTn exchange obtained during all exchange experiments plotted against the cTn concentration in the exchange solution. The following double-exponential curve was fitted to the data points: y = A[1 − exp(−x/k1)] + (100 − A)[1 − exp(−x/k2)], yielded an A value of 68.9%, a k1 value of 0.13 mg/ml, and a k2 value of 1.29 mg/ml. Error bars are shown when larger than symbol size. C: immunoblot of recombinant cTn containing cTnT without (lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7) or with (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8) the Myc tag label. D: average cTnT intensities of four blots plotted against the cTn amount (in ng) loaded per lane for cTnT- and cTnT-myc-containing cTn complexes. Linear regression analysis indicated that the slopes and intercepts did not significantly differ. E: average percentages of cTn exchange in cardioymyocytes after an overnight incubation in exchange solution with 1 mg/ml cTn containing the different pseudo-phosphorylated cTnI species (average values represent cTn exchange experiments in cardiomyocytes isolated from 3 donor hearts). No significant differences were found in exchange percentages between the various cTnI complexes. cTnI-AA, pseudo-dephosphorylated cTnI; cTnI-AD, pseudo-monophosphorylation of Ser24; cTnI-DA, pseudo-monophosphorylation of Ser23; cTnI-DD, pseudo-bisphosphorylated cTnI.