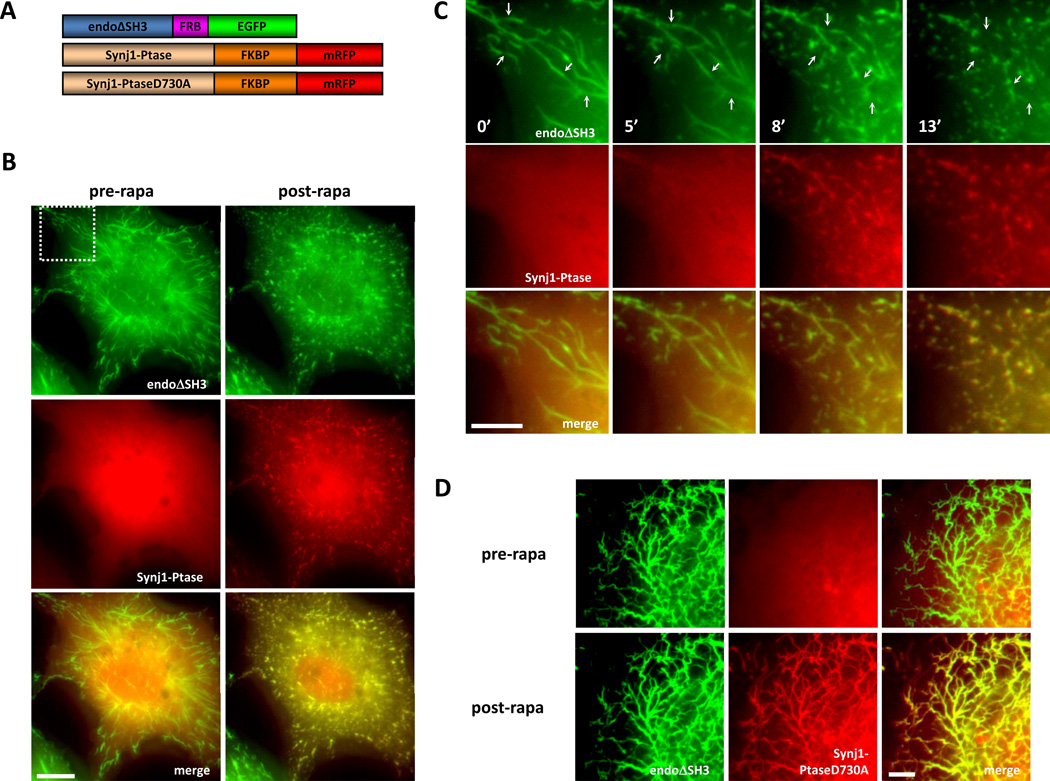
Fig. 3. Acute Recruitment of the Inositol 5-Phosphatase Domain of Synj1 to Endophilin-Induced Tubules Results in Membrane Fragmentation and Condensation.
A) Diagram of the heterodimerization constructs: rat endophilin1 without the SH3 domain (endoΔSH3) is fused to the NH2-terminal side of the FRB domain followed by EGFP; the inositol 5-phosphatase domain of Synj1, either wild type or catalytically dead mutant D730A (Synj1-Ptase, Synj1-PtaseD730A respectively), was fused to the NH2-terminal side of two FKBP domains followed by mRFP. B) In transfected COS-7 cells, Synj1-Ptase shows a diffuse signal before rapalog treatment (pre-rapa). Rapalog treatment results in Synj1-Ptase recruitment to endophilin-induced membrane tubules and fragmentation and condensation of the membrane tubules take place (post-rapa). C) A time-lapse view of the fragmentation and condensation events upon rapalog treatment from a magnified field of the cell seen in B) as indicated by the dotted square. Example fragmentation sites are indicated by the arrows. D) In transfected COS-7 cells, Synj1-PtaseD730A showed diffuse signal before rapalog treatment (pre-rapa). Rapalog addition results in Synj1-PtaseD730A recruitment to endophilin-induced membrane tubules but no fragmentation/condensation events are observed (post-rapa). Scale bars represent B) 10 µm, C) 5 µm, and D) 5 µm. [Reprinted from Developmental Cell, Vol. 20, Chang-Ileto, B., Frere, S.G., Chan, R.B., Voronov, S.V., Roux, A., and Di Paolo, G., Synaptojanin 1-mediated PI(4,5)P2 hydrolysis is modulated by membrane curvature and facilitates membrane fission, Pages No. 206–218, copyright 2011, with permission from Elsevier.]