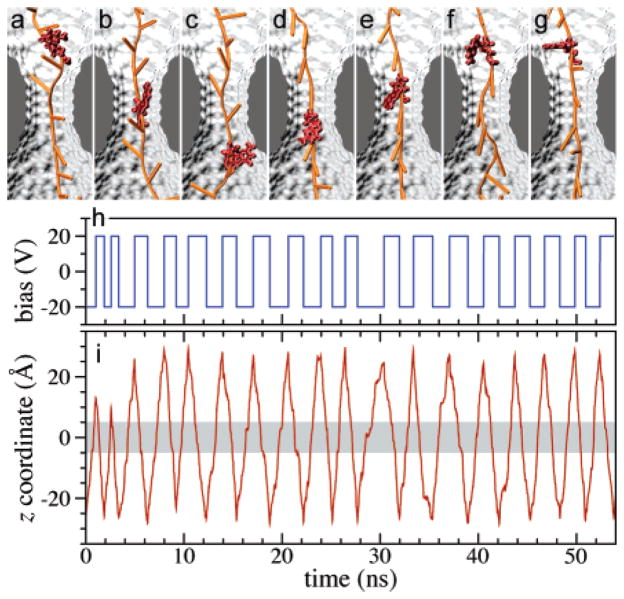
Fig. 6.
DNA motion under alternating external electric field. (a–g) Typical conformations of a DNA strand during one translocation cycle. The conformations of one nucleotide are highlighted for clarity. (a,b) DNA moves down (toward its 5′ end) with its bases tilted up; (c) the base of the highlighted nucleotide reorients after the voltage polarity has been reversed; (d–f) DNA moves up with its bases tilted down; (g) the base of the selected nucleotide changes its orientation again. (h) The profile of the driving potential. Note that the alternating potential is in this simulation aperiodic. (i) The position of the center-of-mass of a DNA nucleotide from the middle of the DNA strand. The shaded area indicates the location of the pore’s constriction region. Adapted from ref. 22.