Figure 8.
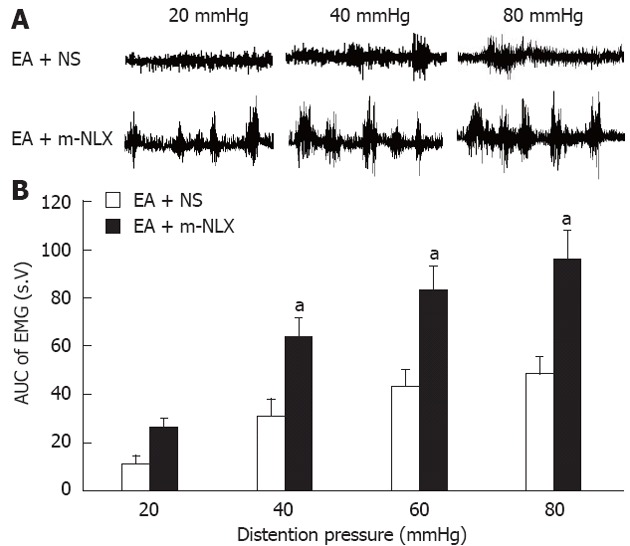
Reversal of electroacupuncture-mediated analgesic effect by naloxone methiodide. The opioid receptor antagonist, naloxone methiodide (m-NLX), or normal saline (NS) was administrated intraperitoneally (5 mg/kg body weight) 30 min before electroacupuncture (EA) application. Electromyographic (EMG) activities were recorded immediately after EA from rats pretreated with m-NLX and NS. A: Examples of EA effects on EMG activities pretreated with NS (top) or m-NLX (bottom); B: Bar graph showing that m-NLX completely blocked the EA-induced analgesic effect. The magnitude of EMG activity was significantly increased by m-NLX treatment at pressure of 40 mmHg, 60 mmHg and 80 mmHg (Tukey post hoc test following two-way repeated measures analysis of variance, n = 6 rats for each group; aP < 0.05 vs EA + NS group).
