Figure 2.
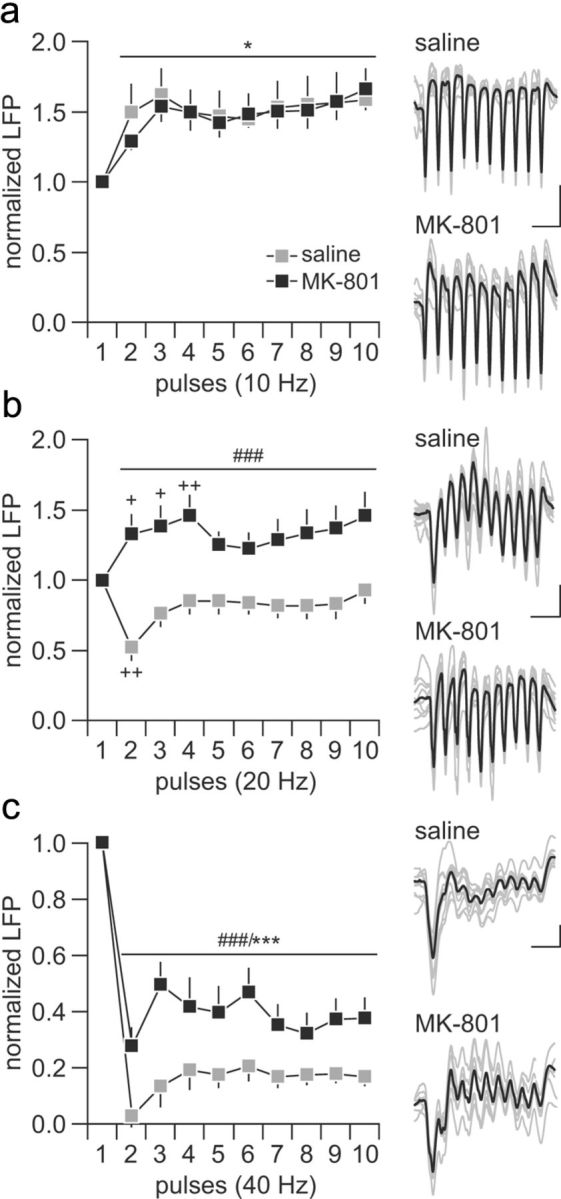
Disruption of ventral hippocampal-induced frequency-dependent prefrontal LFP inhibition by periadolescent MK-801 treatment. a, Saline-treated (n = 12) and MK-801-treated (n = 10) rats exhibited similar degrees of LFP facilitation in the PFC in response to hippocampal train stimulation at 10 Hz (main effect of pulse number, F(9,200) = 2.47, *p < 0.05). b, At 20 Hz, a transient LFP inhibition (++p < 0.005 vs first pulse, least significant difference post hoc test after significant one-way ANOVA) was observed in the PFC of saline-treated rats, whereas recordings from the MK-801-treated group revealed a facilitation (+p < 0.05, ++p < 0.005 vs first pulse, least significant difference post hoc test after significant one-way ANOVA) of the prefrontal LFP response (main effect of treatment, F(1,200) = 12.51, ###p < 0.0005, two-way ANOVA). c, Both saline- and MK-801-treated rats exhibited marked prefrontal LFP depression in response to hippocampal stimulation at 40 Hz. However, a significant attenuation of the magnitude of the 40 Hz-induced LFP inhibition was observed in the MK-801-treated group (main effect of pulse number, F(9,200) = 30.57, ***p < 0.0005; main effect of treatment, F(1,200) = 57.7984, ###p < 0.0005, two-way ANOVA). Insets are example traces of ventral hippocampal-induced LFP facilitation and suppression recorded in the PFC illustrating the effects shown in a–c. Calibration: a, 5 mV, 200 ms; b, 5 mV, 100 ms; c, 3 mV, 50 ms.
