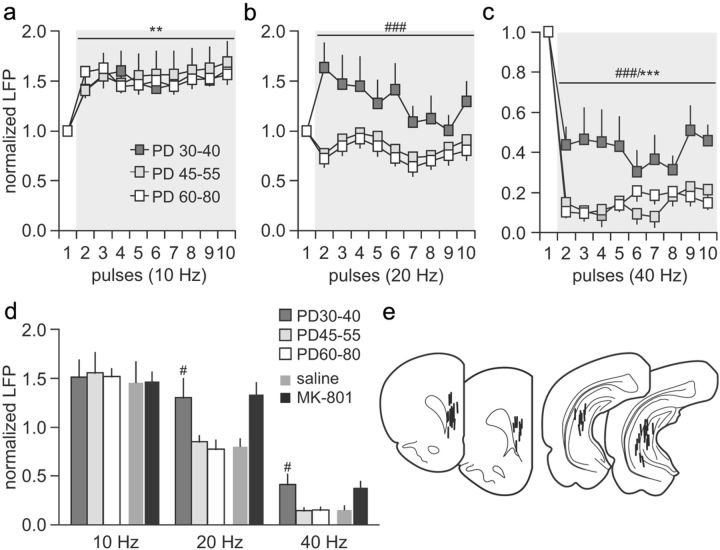
Figure 4.
Developmental regulation of ventral hippocampal-induced facilitation and suppression of LFP transmission in the PFC. a, The pattern of prefrontal LFP facilitation to ventral hippocampal stimulation at 10 Hz were indistinguishable among rats from P30–P40 (n = 10), P45–P55 (n = 8), and P60–P80 (n = 6) (main effect of pulse number, F(9,210) = 2.55, *p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA). b, At 20 Hz, a facilitation of LFP response was observed only in the P30–P40 age group PFC. Note that such facilitation resembles that observed in the adult PFC from adolescent MK-801-exposed rats (see Fig. 2b). In contrast, a characteristic 20 Hz-induced transient LFP attenuation was observed in the PFC of P45–P55 and P60–P80 age groups (main effect of age, F(2,210) = 23.49, ###p < 0.0005, two-way ANOVA). c, Similarly, the P30–P40 PFC exhibited a marked attenuation of the 40 Hz-induced LFP suppression, whereas the magnitude of prefrontal inhibition obtained in the P45–P55 age group was identical to that from the adult PFC (main effect of pulse number, F(9,210) = 20.88, ***p < 0.0005; main effect of age, F(2,210) = 25.61, ###p < 0.0005, two-way ANOVA). d, Bar graph summarizing the magnitude of hippocampal-induced LFP facilitation and inhibition in the PFC across age groups. The average values were calculated from pulses 2 to 10 as shown in a–c (i.e., marked in gray). Data from adolescent saline- and MK-801-treated animals (from Fig. 2) were included for comparison. Both the degrees of LFP facilitation at 20 Hz and LFP attenuation at 40 Hz observed in the periadolescent MK-801-treated group resemble those from the P30–P40 age group (#p < 0.02 vs P45–P55, vs P60–P80, vs saline, least significant difference post hoc test after significant one-way ANOVA). e, Location of all recording and stimulation sites determined by means of histological analyses from Nissl-stained sections. PD, Postnatal day.