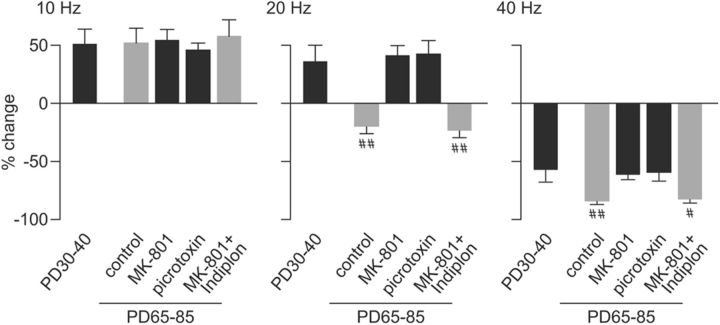
Figure 7.
Summary of the prefrontal field potential response to ventral hippocampal train stimulation at 10, 20, and 40 Hz across the different experimental groups. The percentage change of prefrontal LFP response was calculated from the mean amplitude value of pulses 2 to 10 relative to pulse 1 as shown in Figures 4–6. The control group comprised saline-treated and adult naive animals. The MK-801 group includes all periadolescent MK-801-treated rats from Figures 2 and 6 (aCSF group). Note that the characteristic facilitation of prefrontal response to 10 Hz stimulation is not developmental regulated and remained unchanged after adolescent MK-801 exposure or single acute administration of picrotoxin into the PFC (p = 0.998, one-way ANOVA). In contrast, PFC responses to 20 and 40 Hz train stimulation are developmentally regulated and sensitive to periadolescent MK-801 treatment and local prefrontal GABAA receptor blockade. In fact, MK-801-treated animals exhibited the same pattern of prefrontal responses undistinguishable from the developmentally immature P30–P40 PFC and those recorded in the presence of local GABAA receptor blockade. Importantly, single microinfusion of the GABAAα1-receptor-positive allosteric modulator Indiplon into the PFC was sufficient to acutely restore the 20 and 40 Hz-induced inhibitory prefrontal field potential response to control levels (#p < 0.02, ##p < 0.005 vs P30–P40, periadolescent, MK-801, or picrotoxin, least significant difference post hoc test after significant one-way ANOVA: F(4,55) = 8.94, p < 0.00005 for the 20 Hz response; F(4,55) = 5.96, p < 0.0005 for the 40 Hz response). PD, Postnatal day.