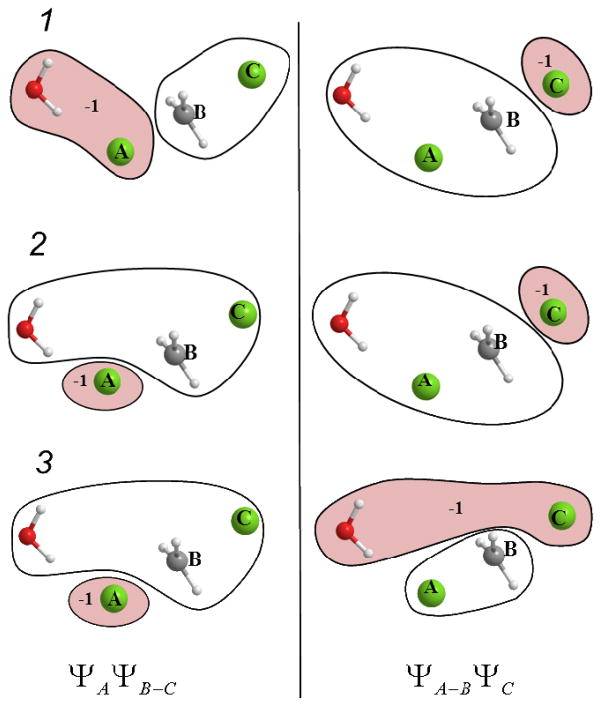
Figure 1.
Possible choices of assigning a QM water molecule to the partitions of the diabatic states illustrated for the Cl− + CH3Cl system. The water molecule can be either assigned to group A, B or C when defining the reactant and product diabatic states, resulting in the above depicted three possibilities: 1, 2, and 3. The first column shows the reactant state decompositions with ΨA ΨB–C, and the second column corresponds to the product state partitioning, ΨA–B ΨC. The three choices for the partitioning of the water molecule are 1: including the water molecule in the same partition with group A, 2: including the water molecule in the same partition with the central group B, or 3: including the water molecule in the same partition with group C. The negatively charged partition is indicated by colored background and the displayed charge value (e).