Figure 2. Different groups of neurons are sensitive to ethanol exposure at specific developmental stages.
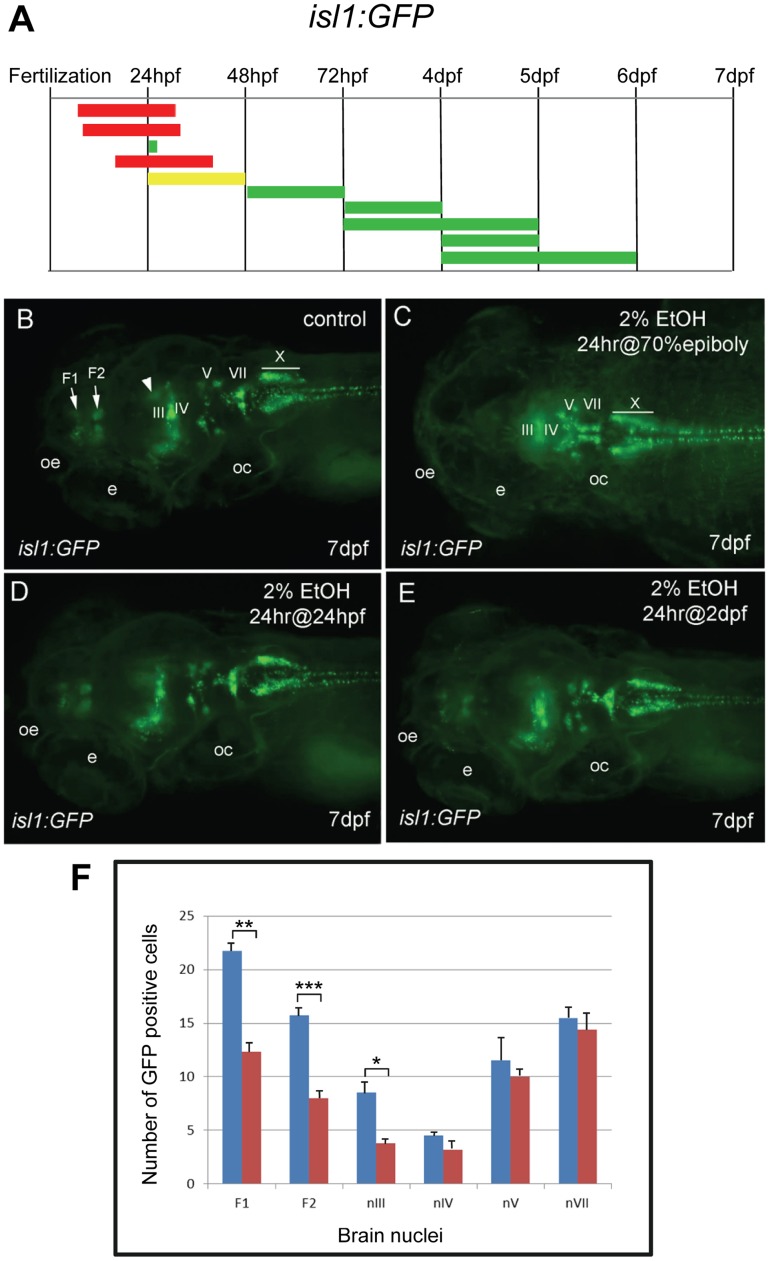
A, the duration and embryonic stage of 2% ethanol treatments illustrated with colored bars for Tg(isl1:GFP) embryos, as described in Fig. 1. B−E, dorsal views of Tg(isl:GFP) larva at 7 dpf. B, is the control. GFP expression was evident in the forebrain nuclei (F1 and F2 arrows), the mesencephalic cluster (arrowhead) and cranial motor nuclei III, IV, V, VII, and X (labeled). C, GFP expression in the forebrain and mesencephalic cluster was absent, and GFP expression in cranial motor nuclei III and IV was reduced (labeled) after 2% ethanol treatment for 24 hrs at the 70% epiboly stage. D, E, GFP expression was largely normal after treatment with 2% ethanol for 24 hrs at 24 hpf (D) and for 24 hrs at 48 hpf (E). Eyes (e), otic capsule (oc), olfactory epithelium (oe). F, the average numbers of GFP-positive cells in individual brain nuclei of control (n = 10) and ethanol-treated (n = 10) embryos. A highly significant reduction in GFP-expressing cells in the two forebrain nuclei, F1 (p = 0.001) and F2 (p<0.001), and cranial motor nucleus III (p<0.05) was observed. In contrast, a slight reduction in GFP cells in motor nuclei IV, V and VII was not significant. Error bars represent SEM. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.
