Figure 4. Neurons are sensitized to ethanol in med12 mutant embryos. A−C.
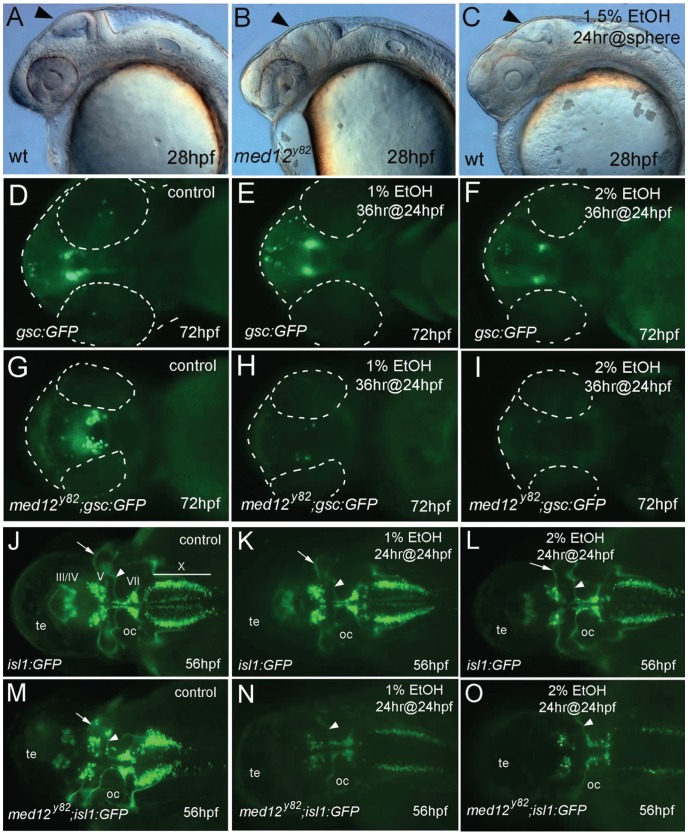
, 28 hpf embryos. A, wild-type (wt), B, med12y82 mutant, and C, wt embryo treated at sphere stage with 1.5% ethanol for 24 hrs. Note the similarly retarded brain development in the med12y82 and ethanol treated embryos (arrows). D−I, ventral views at 72 hpf of Tg(gsc:GFP) embryos (D, E, F) and med12y82; Tg(gsc:GFP) embryos (G, H, I). D, G, control embryos. E, H, treated with 1% ethanol for 36 hrs at 24 hpf. F, I, treated with 2% ethanol for 36 hrs at 24 hpf. Embryos and eyes are outlined (dashed white lines). J−O, Tg(isl1:GFP) embryos (J, K, L) and med12y82; Tg(isl1:GFP) embryos (M, N, O) at 56 hpf, dorsal views. J, M, control embryos. K, N, treated with 1% ethanol for 24 hrs at 24 hpf. L, O, treated with 2% ethanol for 24 hrs at 24 hpf. GFP-expressing cranial motor neurons (labeled) diminished in med12y82; Tg(isl1:GFP) embryos, especially in nuclei III and IV. A reduction of nucleus V neurons in med12y82; Tg(gsc:GFP) embryos treated with ethanol is illustrated by the elimination of the prominent nV axons (arrows). In contrast, the prominent nVII axons remained intact (arrowheads). Otic capsule (oc), tectum (te).
