Figure 5.
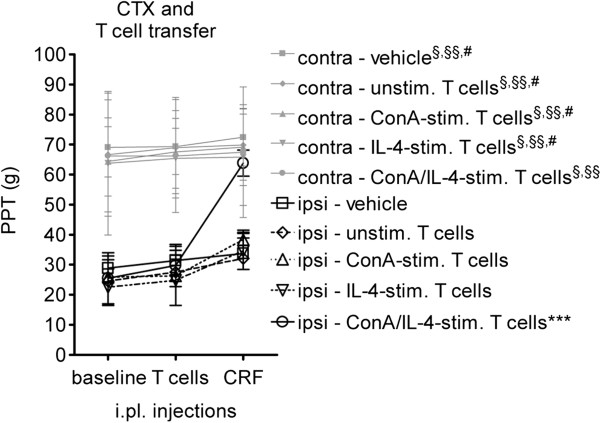
Transfer of cytokine-stimulated T cells restores CRF-induced antinociception in immunosuppressed rats with hindpaw inflammation. Cyclophosphamide (CTX)-pretreated rats with CFA-induced hindpaw inflammation were injected i.pl. with untreated, ConA-, IL-4- or ConA/IL-4-pretreated T cells. PPT were determined in the ipsilateral and contralateral paw at baseline, after T cell transfer, and after i.pl. CRF injection. Controls received i.pl. vehicle. Data represent means ± SD (n = 7–8 animals per group). PPT values were analyzed for effects of the injection (baseline, T cell transfer, and CRF-injection) and between paws (ipsi versus contralateral) using Two-Way RM ANOVA and Bonferroni’s Test. §, Ipsilateral PPT are significantly lower than contralateral values at baseline (P < 0.001); §§, Ipsilateral PPT are significantly lower than contralateral values after T cell-injection (P < 0.001); #, Ipsilateral PPT are significantly lower than contralateral values after CRF-injection (P < 0.001). Effects of treatment (vehicle versus unstimulated, ConA-, IL-4-, and ConA/IL-4-stimulated T cells) and injection (baseline, T cell transfer, and CRF-injection) on ipsilateral PPT values were analyzed using Two-Way RM ANOVA and Bonferroni’s Test. ***, Ipsilateral PPT are significantly elevated in recipients of ConA/IL-4-stimulated T cells after CRF-injection (P < 0.001).
