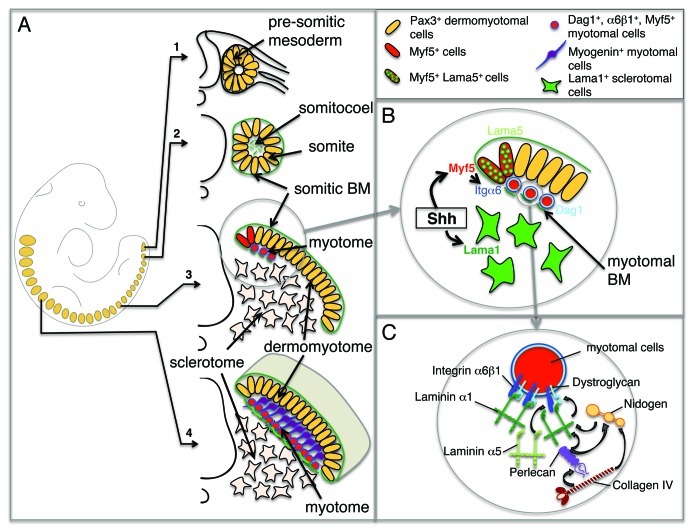
Figure 2. Assembly of the myotomal basement membrane. (A) Myogenesis along the antero-posterior axis of the mouse embryo. A schematic representation of an E9.5 mouse embryo is shown on the left with somites indicated in orange. Panels 1–4 depict the maturation of somites along the rostro-caudal axis with pluripotent, undetermined Pax3+ cells in the anterior presomitic mesoderm (1), Pax3+ epithelial somitic cells and fragment of laminins secreted in the somitocoele (2), the initiation of myotome formation following Myf5 activation in the dorsal medial lip of the dermomyotome. Myf5+ cells begin assembling the myotomal BM as they translocate to the myotome (3), in rostral somites, the myotome is separated from the sclerotome by a fully assembled myotomal BM (shown in green). Cells deeper within the myotome begin differentiating and expressing myogenin (4). (B) Magnification of the steps taking place in the dorsal medial lip of the dermomyotome illustrated in (3). Shh induces the activation of Myf5 in the dermomyotome. Myf5+ cells translocate to the myotome and upregulate α6β1 integrin and dystroglycan, allowing the initiation of the myotomal BM assembly using primarily laminin α1 produced by sclerotomal cells, and laminin α5 produced by the dorsal medial lip of the dermomyotome. (C) Magnification of a myotomal cell illustrating the steps leading to the assembly of the myotomal BM. Laminin-111 polymers are shown binding to and assembling at the surface of Myf5+ myotomal cells. The nascent ultrastructure is stabilized by the incorporation of nidogen and perlecan that link collagen IV to laminin chains. Laminin-511 is likely to be intercalated in the myotomal BM.
