Figure 1. Design of Ras FRET sensors.
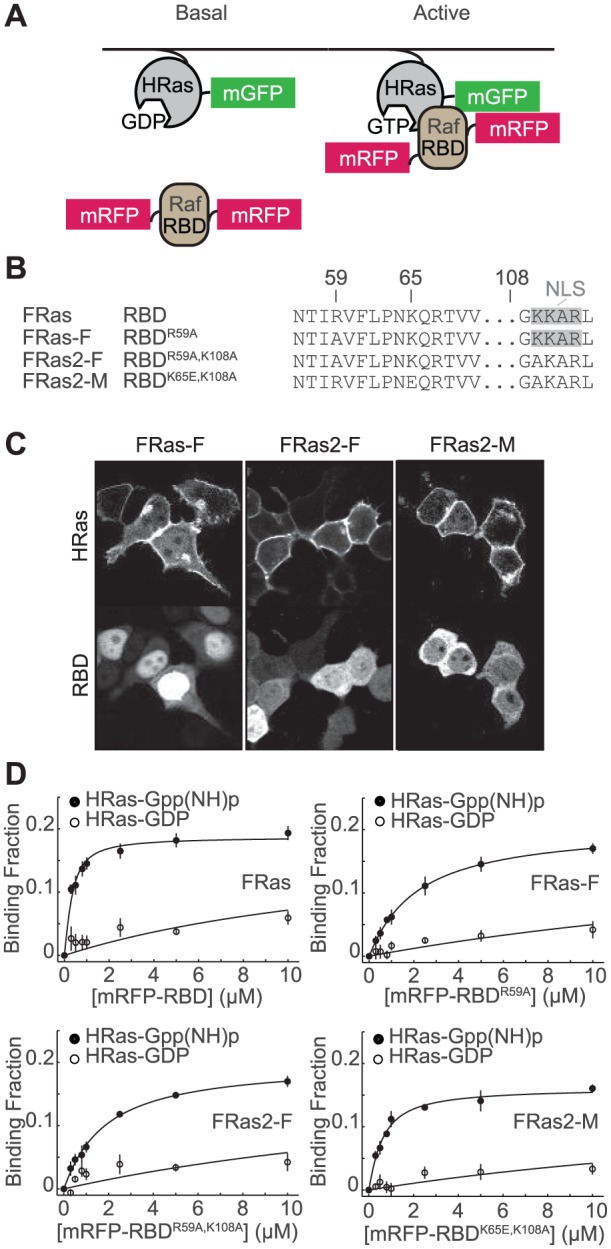
(A) Schematics of Ras FRET sensors. mEGFP was tagged to the N terminus of HRas, and mRFP was attached to both termini of Ras binding domain of Raf1 (RBD), which binds selectively to active Ras. When HRas is activated, it binds to RBD, increasing FRET between mEGFP and mRFP. (B) Abbreviated amino acid sequence of RBD (WT), RBDR59A, RBDR59A,K108A and RBDK65E,K108A, highlighting the mutations introduced in the RBD sequence to produce different Ras sensor acceptors. (C) Distribution of donor and acceptor for FRas-F, FRas2-F, and FRas2-M expressed in 293T cells. (D) Measurements of the affinity between sfGFP-tagged HRas and mRFP-tagged RBD. The binding fraction was measured with 2pFLIM as a function of the RBD concentration (average of 3–5 independent experiments). The dissociation constants between HRas and RBD mutations are summarized in Table 1.
