Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree constructed with the sequences obtained by Method D (E1 region).
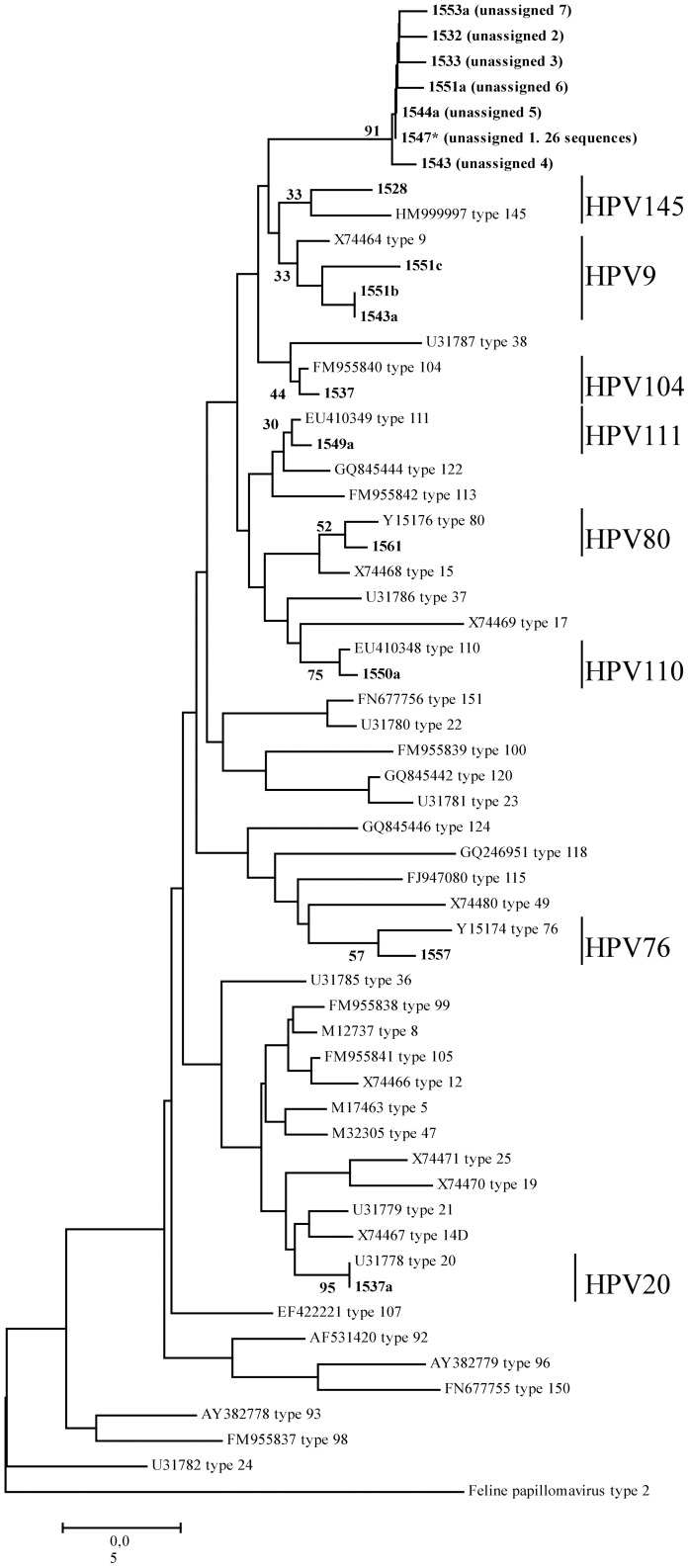
The tree was constructed using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Kimura 2-parameter model. The sequences identified in this study are in bold. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. Only selected bootstrap values related to the studied sequences are displayed. The Beta HPV prototypes reported in the phylogenetic tree are: HM999997 type 145, X74464 type 9, U31787 type 38, FM955840 type 104, EU410349 type 111, GQ845444 type 122, FM955842 type 113, Y15176 type 80, X74468 type 15, U31786 type 37, X74469 type 17, EU410348 type 110, FN677756 type 151, U31780 type 22, FM955839 type 100, GQ845442 type 120, U31781 type 23, GQ845446 type 124, GQ246951 type 118, FJ947080 type 115, X74480 type 49, Y15174 type 76, U31785 type 36, FM955838 type 99, M12737 type 8, FM955841 type 105, X74466 type 12, M17463 type 5, M32305 type 47, X74471 type 25, X74470 type 19, U31779 type 21, X74467 type 14D, U31778 type 20, EF422221 type 107, AF531420 type 92, AY382779 type 96, FN677755 type 150, AY382778 type 93, FM955837 type 98, and U31782 type 24. A feline papillomavirus type 2 (EU796884) was included as an outgroup. Sample 1547, marked with* had identical sequences with other 25 samples (IDs 1529, 1530, 1531, 1532a, 1534, 1535, 1538, 1539, 1540, 1542, 1544, 1545, 1546, 1548, 1549, 1550a, 1553, 1554, 1554a, 1555, 1556, 1568, 1566, 1571), not included in the tree. Sequences obtained from different clones are indicated by alphabetical code (ID sample “a”, “b”).
