Fig. 4.
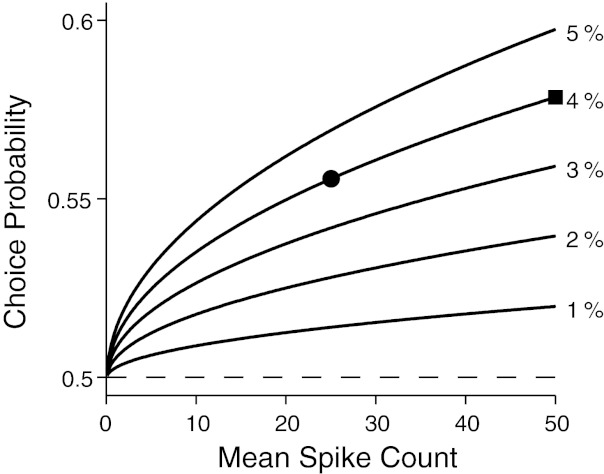
Relationship between length of measurement interval and CP. Length of the measurement interval is represented as the mean spike count during the interval (x-axis) assuming that the mean spike count is proportional to the length of the measurement interval. CP at a point on each curve was numerically calculated by applying an ROC analysis to a pair of Poisson probability mass functions. The mean of one of the probability functions was the value on the x-axis, and the other was higher by the amount indicated at the end of each curve. Horizontal dashed line indicates no correlation between the neuronal response and behavior.
