Figure 4. hxk1 mutants are hyperfilamentous on filamentation inducing solid media.
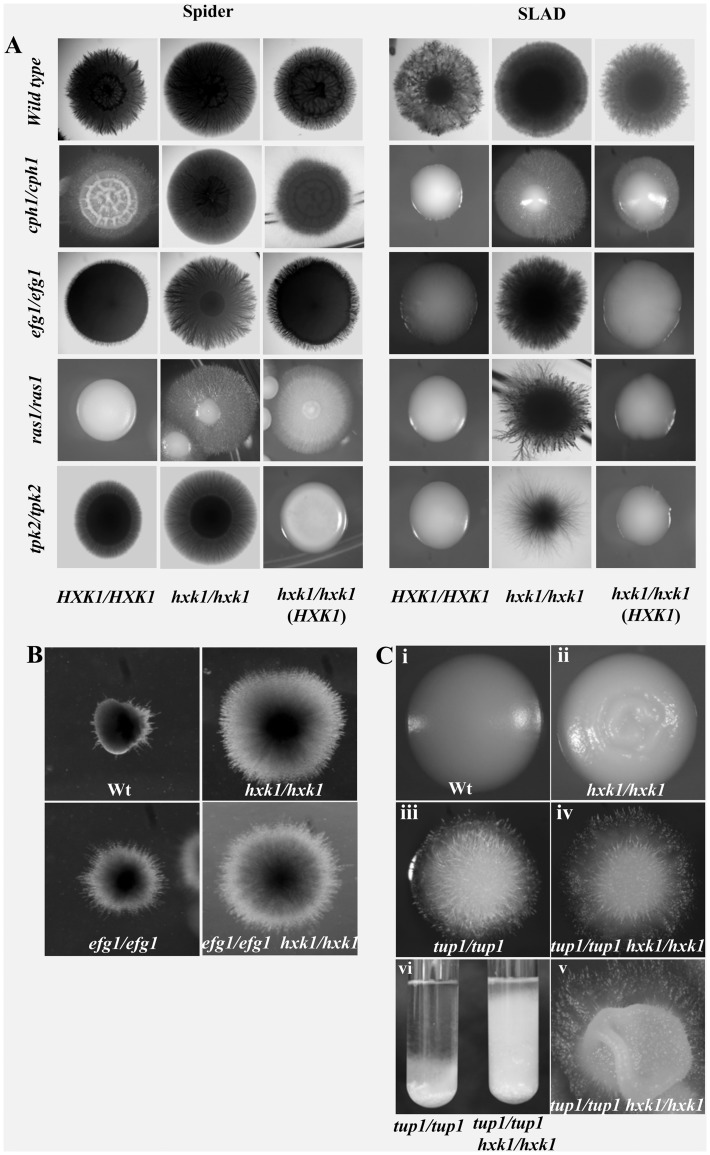
A) Hyphae formation on Spider and SLAD plates. All hxk1 mutants including efg1/hxk1 showed hyperfilamentation. Strains were incubated at 37°C for 7 days in case of spider and 10 days in case of SLAD plates. Wild-type CAF2–1 (HXK1/HXK1); hxk1 mutant, H8–1–103 (hxk1/hxk1); cph1 mutant, A11–1 (cph1/cph1); double mutant of cph1/hxk1, AN8–1–16 (cph1/cph1 hxk1/hxk1); efg1 mutant, HLC52 (efg1/efg1); double mutant of efg1/hxk1 HLC67–16–1–9 (efg1/efg1 hxk1/hxk1); tpk2 mutant, TPO7.4 (tpk2/tpk2); double mutant of tpk2/hxk1, AS1–3–1–8 (tpk2/tpk2 hxk1/hxk1) and their respective complemented strains in which one functional copy of HXK1 was reintroduced in the native locus. B) efg1/efg1 hxk1/hxk1 double mutant showed hyperfilamentation under embedded conditions. Cells of wild-type, CAF2–1, hxk1/hxk1, efg1/efg1, efg1/efg1hxk1/hxk1, mutants were grown in YPD for 5 hrs at 30°, washed in sterile water and mixed with molten CM Agar (with 1% Tween-80) plated and grown for 3 days at 25°C. efg1 hxk1 double mutant showed hyperfilamentation when compared to hxk1 or efg1 single mutants (EFG1 is reported to be a negative regulator of filamentation under micro-aerophillic/embedded conditions). C) tup1/hxk1 double mutant showed growth pattern slightly different from tup1 mutant. Wild type (i), hxk1 mutant (ii), tup1(iii) and tup1/hxk1(iv) mutants colonies were grown on YPD solid and liquid medium for 3 and 2 days respectively at 30°C. tup1/hxk1double mutant shared most of the features with a tup1 single mutant (iii, iv) on YPD plates, but in some colonies of the double mutant a wavy, afilamentous fringe could be observed at the centre(v). In YPD broth the tup1 single mutant grew in clumps having the tendency to settle at the bottom, the tup1/hxk1 double mutant showed uniform turbidity throughout the culture with clumps in the bottom (vi).
