Figure 3. Distribution of the size of integrase-target DNA complexes.
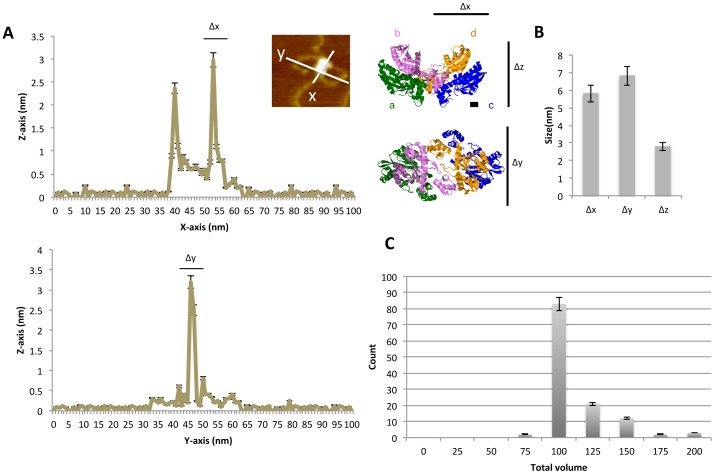
(A) Line graphs showing representative measurement of the diameter across a twin-like structure of integrase bound to the DNA strands along the x- and y-axes. The upper and lower graphs show the longer and shorter diameter of the twin-globule structure individually. The photo in the inset is identical to the photo shown in Figure 1C. To the right are 3D crystal structures of integrase obtained from X-ray data (PDB 1K6Y) [15]. Four integrase molecules associate in a tetrameric fashion in the DNA binding form. Monomers are represented by (a) green, (b) purple, (c) blue, and (d) orange. The diameter of the integrase dimer along the y-axis is approximately 5 nm, measured by the distance between two amino acids (E69 of c and I191 of d), represented in red. The thickness along the z-axis is approximately 3 nm, measured by the distance between Q62 of c and C65 of d, represented in red. These values were determined using Jmol. The scale bars are equivalent to approximately 1 nm. (B) Size of tetrameric integrase along the x-, y-, and z-axes (n = 123). (C) Histogram showing the distribution of the estimated volume (nm3) of the twin-like integrase structures bound to target DNA strands (n = 123).
