Fig. 4.
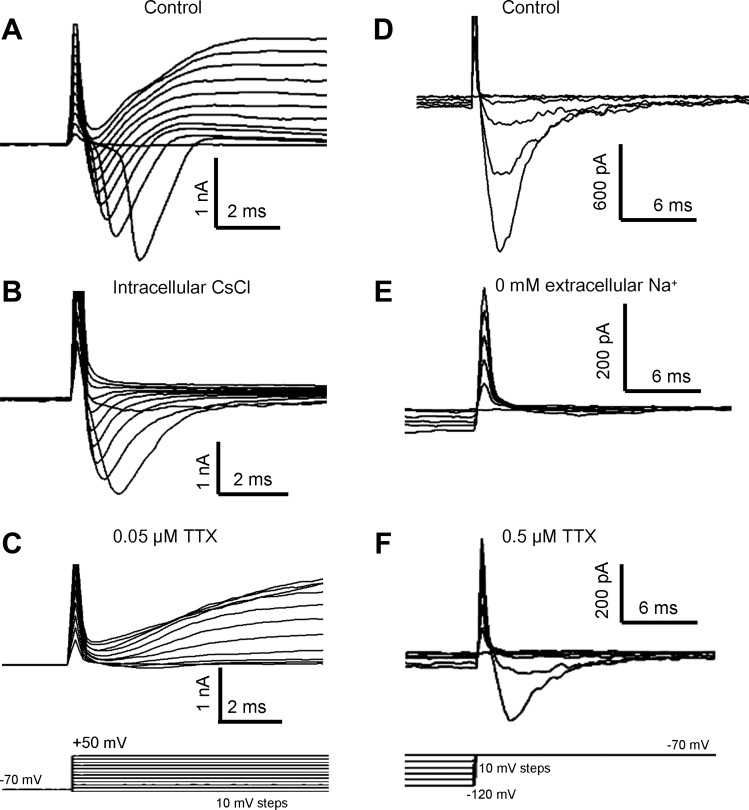
Whole cell voltage-dependent currents in GG neurons. A–C: depolarization to test potentials in the range of −50 to +50 mV from a holding potential of −70 mV (C, bottom) induced membrane currents in GG neurons. A: depolarization pulses evoked transient inward currents and sustained outward currents. B: outward currents were absent when patch pipettes were filled with 110 mM Cs+ and 30 mM tetraethylammonium. C: bath application of 50 nM tetrodotoxin (TTX) abolished most inward currents. D–F: repolarization back to −70 mV from hyperpolarized test potentials in the range of −120 to −100 mV (F, bottom) elicited transient inward currents (D). These inward currents were eliminated by removal of extracellular Na+ (E) but remained in the presence of 0.5 μM TTX (F). Traces shown are from different neurons but are representative.
