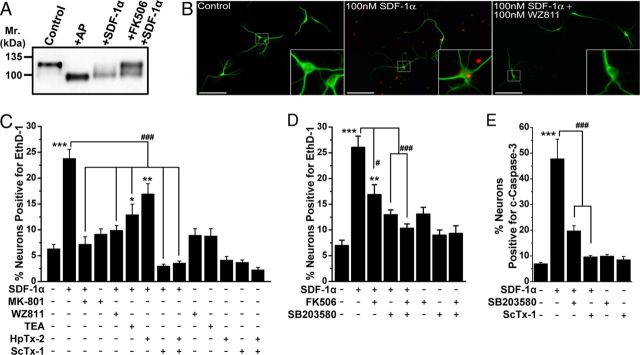
Figure 7.
Sustained SDF-1α treatment results in the induction of neuronal apoptosis that is dependent on CXCR4–calcineurin/p38 MAPK–Kv2.1 signaling. A, Immunoblot analysis showing dephosphorylation of Kv2.1 protein during sustained SDF-1α treatment (100 nm, 3 h) of cultured rat hippocampal neurons, which was attenuated by pretreatment with FK506 (10 μm). B, Representative images of cultured hippocampal neurons immunostained with anti-MAP2 (green) antibody and EthD-1 (red), showing increased EthD-1-positive nuclei, indicative of dead neurons, during sustained SDF-1α treatment (100 nm, 3 h). Scale bars, 50 μm. C, Quantification of neuronal death in response to various drug treatments, as determined by percentage of EthD-1-positive neurons. Sustained SDF-1α-induced neuronal death was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with WZ811 (100 nm), the nonspecific K+ channel blocker TEA (70 mm), and the Kv2.1 channel-blocking toxin ScTx-1 (100 nm) but not by the Kv4.2 channel-blocking toxin HpTx-2 (100 nm). D, Sustained SDF-1α-induced neuronal death was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with FK506 (10 μm) and the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (1 μm). E, Sustained SDF-1α-induced neuronal death is apoptotic in nature and is dependent on p38 MAPK–Kv2.1 signaling. Quantification of c-caspase-3-positive neurons after various drug treatments. Sustained SDF-1α-induced (100 nm, 3 h) increase in the number of c-caspase-3 nuclei-stained neurons was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with SB203580 (1 μm) and ScTx-1 (100 nm). All data in C–E are presented as mean ± SEM (n = >500 neurons from 4 independent experiments). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 versus untreated conditions; #p < 0.05 and ###p < 0.001 compared with only SDF-1α treatment (one-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni's correction).