Fig. 1.
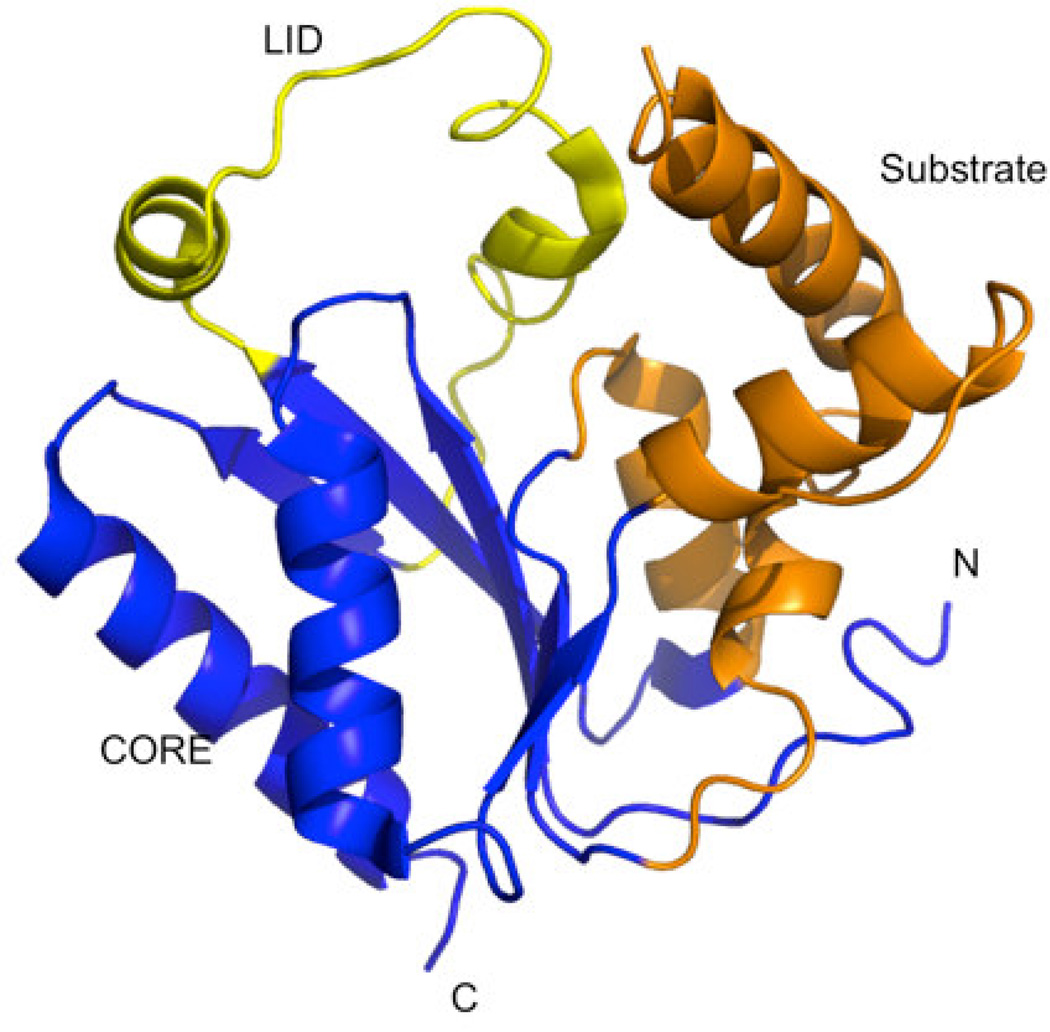
Crystal structure of human PMK (PDB ID 3ch4)[22] showing the different functionally relevant regions of the protein. The LID region caps the active site where phosphate transfer occurs, and contains catalytic residues needed for stabilizing the negative charge buildup in the phosphate transfer transition state. The CORE and Substrate domains are proposed to participate in significant domain rearrangements upon binding the substrates M5P and MgATP.[15]
