Fig. 3.
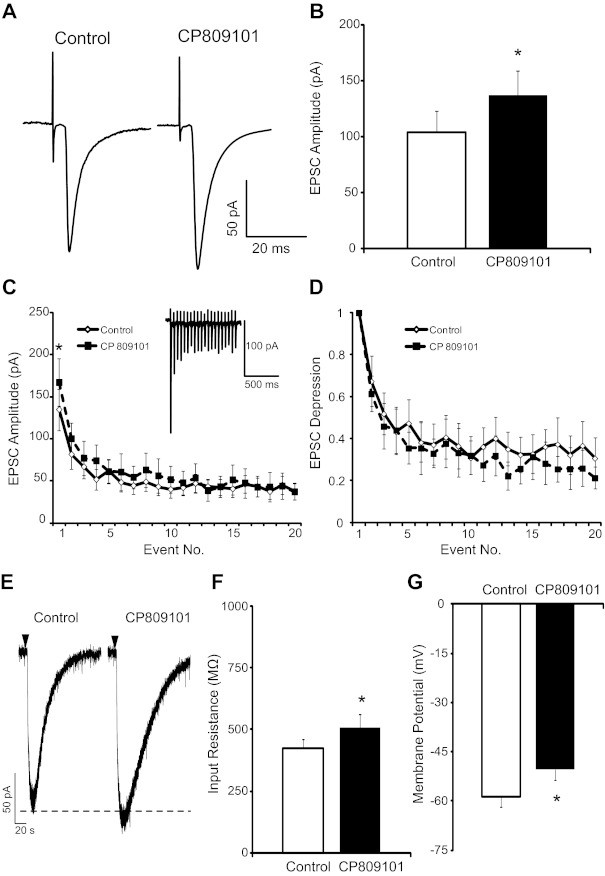
5-HT2CR activation augments TS excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs). A: representative traces of TS-EPSCs (30 sweeps, averaged) evoked at 0.5 Hz from a single cell during control and 5-HT2CR activation by CP809101. Note the augmented amplitude after the 5-HT2CR agonist CP809101 (50 μM, 5 min). B: group raw data of TS-EPSC amplitude during control and CP809101 (50 μM, 5 min, n = 7). C: TS stimulation at 20 Hz produced use-dependent depression (◇), which was maintained after CP809101 (■, n = 7). An example of the observed use-dependent depression is shown in inset. There was an increase in event 1 amplitude with CP809101 (P < 0.05) but no change in amplitude of subsequent events. D: relative magnitude of EPSC depression from the 1st event (plotted as 1). E: brief application of AMPA (1 mM, 50 ms) evoked inward currents that were increased by CP809101. Downward arrowhead depicts application of AMPA. F and G: 5-HT2CR activation with CP809101 (n = 7) increased input resistance (F) and depolarized membrane potential (G). *P < 0.05.
