Figure 2.
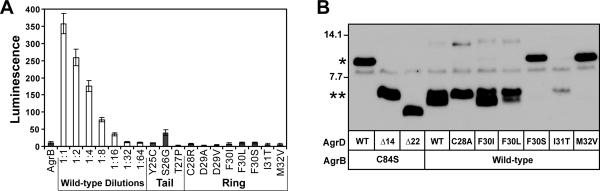
Point mutations in the AIP-encoding sequence of AgrD. A. AIP activation bioassay with the mutations in the AIP-encoding region of AgrD. AgrB and AgrD point mutants were expressed from pEPSA5 in E. coli, supernatants were added to the ROJ143 AIP-lux reporter, and luminescence was measured to detect the presence of AIP. B. Peptidase assay of select AIP point mutations. AgrB cleavage of the AgrD C-terminus was tested by separating cell lysates from E. coli expressing T7-AgrB and His6-tagged AgrD mutations by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using anti-His antibodies. “*” indicates full-length His6-AgrD and “**” indicates cleaved His6-AgrD with the C-terminus removed, and the control lanes are described in Figure 1.
