Figure 3.
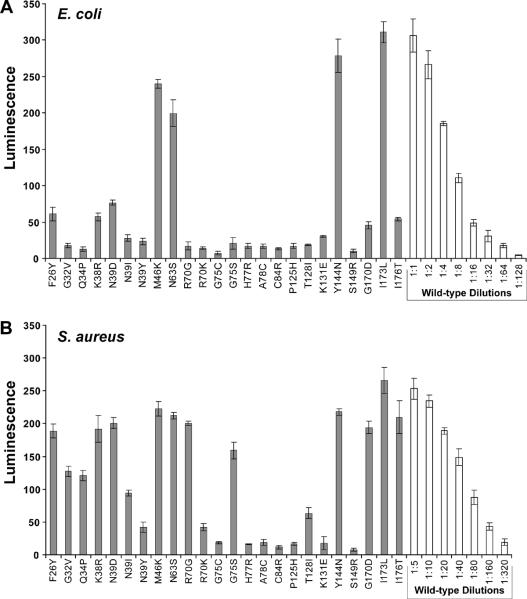
AIP activation bioassay with AgrB point mutants. A. Bioassay for AIP using supernatants from E. coli expressing mutated pEPSA5-agrBD. X-axis labels indicate the AgrB mutation being tested. Supernatants were filtered, added to the ROJ143 reporter strain for one hour and bioluminescence was measured. B. AIP bioassay of same AgrB point mutants expressed in S. aureus Δagr mutant strain AH1292. Supernatants from S. aureus were filtered and diluted 1:10 in TSB before being added to the ROJ143 reporter. Serial dilutions of wild-type supernatants were used to calculate the relative percent of AIP produced in each mutant compared to wild-type pEPSA5-agrBD (see Table 2). Experiments were performed in triplicate and bars represent the standard error of the mean.
